New research reveals that functional connectivity can distinguish between various disease subtypes.
Not only is major depressive disorder (MDD) one of the most prevalent mental health conditions, affecting more than 8% of the U.S. population, but it also manifests in diverse ways among individuals. Although recent research has made progress in understanding the neurological foundations of various depression subtypes, thereby paving the way for improved treatments, there is still much to explore. Now, a new study in Biological Psychiatry, published by Elsevier, identifies multiple subtypes of MDD using brain imaging.
John Krystal, MD, Editor of Biological Psychiatry, said of the work, "We have long known that disorders like major depressive disorder are highly heterogeneous. This study in a large sample of depressed patients provides leads that can be pursued in subtyping depression on the basis of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) tests that measure the degree of coordination across brain regions, also known as 'functional connectivity.'"
The researchers used resting-state fMRI collected at multiple clinical sites from a large cohort of more than 1,000 MDD patients and over 1,000 healthy controls (HC). The study used the so-called normative model, which uses data from a large reference population to quantify individual deviations, much like the growth charts used by pediatricians. The researchers examined the functional connectivity among brain regions and mapped individual functional deviations in the MDD patients compared to this normative prediction across the lifespan.
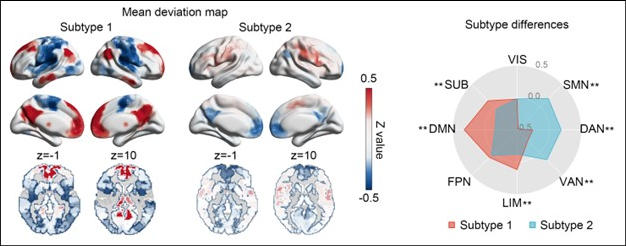
Brain imaging maps and a functional deviation map of the two depression subtypes across brain regions. Credit: Biological Psychiatry
Senior author Mingrui Xia, PhD, from Beijing Normal University, said, "This approach led to the identification of two reproducible neurophysiological subtypes exhibiting distinct deviation patterns, depressive item scores, and longitudinal treatment predictability."
One subtype of patients showed severe positive deviations – indicating increased brain connectivity – in the default mode network, limbic, and subcortical areas, and negative deviations in the sensorimotor and attention areas. The second subtype of patients featured a milder and opposite pattern of deviation, highlighting the heterogeneity of depression at the neurophysiological level. The authors speculate that the altered activity could be related to the tendency to ruminate in people with MDD.
The work is particularly exciting in that it moves the field toward finding biomarkers, or biological markers, of depression, which currently relies on patient-reported clinical symptoms for diagnosis, treatment, and prognostics. Biomarkers could offer a way to improve all these aspects of treatment for MDD.
Dr. Xia went on to say, "These findings shed light on the diverse neurobiological mechanisms from a connectomics perspective underlying the complex clinical heterogeneity observed in individuals with depression. The implications of this research are far-reaching, providing valuable insights into the development of imaging-based candidate biomarkers. These biomarkers have the potential to guide future precise diagnostic and treatment strategies tailored to each patient's specific neurophysiological subtype."
Dr. Xia noted, "By embracing the concept of neurophysiological subtypes, we can potentially revolutionize the field of mental health by enabling clinicians to personalize treatments based on an individual's unique connectome characteristics. This approach opens up new avenues for precision medicine and holds the promise of improving therapeutic interventions for depression."
Reference: "Mapping Neurophysiological Subtypes of Major Depressive Disorder Using Normative Models of the Functional Connectome" by Xiaoyi Sun, Jinrong Sun, Xiaowen Lu, Qiangli Dong, Liang Zhang, Wenxu Wang, Jin Liu, Qing Ma, Xiaoqin Wang, Dongtao Wei, Yuan Chen, Bangshan Liu, Chu-Chung Huang, Yanting Zheng, Yankun Wu, Taolin Chen, Yuqi Cheng, Xiufeng Xu, Qiyong Gong, Tianmei Si and Mingrui Xia, 7 June 2023, Biological Psychiatry.
DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2023.05.021
News
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]