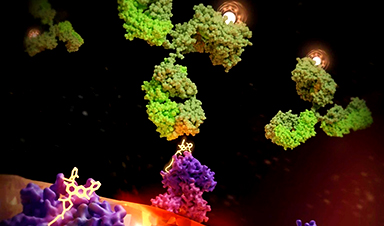
Scientists at UC San Francisco have developed a revolutionary cancer treatment that precisely targets tumors with radiation while sparing healthy tissues.
By using a KRAS-targeting drug to mark cancer cells and attaching a radioactive antibody to eliminate them, this approach has successfully wiped out tumors in mice without the usual side effects of radiation.
Targeted Radiation: A Breakthrough in Cancer Treatment
Radiation is one of the most powerful tools for destroying tumors, but traditional radiation therapy can’t distinguish between cancerous and healthy cells, often causing harmful side effects.
Now, researchers at UC San Francisco have developed a way to make radiation more precise. Their new approach combines a specialized drug that marks cancer cells with a radioactive antibody that directly targets and destroys them.
In studies on mice, this treatment successfully eliminated bladder and lung tumors without causing common radiation side effects like lethargy or weight loss.
“This is a one-two punch,” said Charly Craik, PhD, a professor of pharmaceutical chemistry at UCSF and co-senior author of the study, published recently in the journal Cancer Research. “We could potentially kill the tumors before they can develop resistance.”
A Cancer Drug Becomes a Molecular Flag
The foundation for this breakthrough was laid a decade ago when UCSF’s Kevan Shokat, PhD, discovered how to target KRAS, a notorious cancer-causing protein. When mutated, KRAS drives uncontrolled cell growth and is responsible for up to a third of all cancers.
Shokat’s breakthrough led to the development of drugs that latched onto cancerous KRAS. But the drugs could only shrink tumors for a few months before the cancer came roaring back.
The drugs stayed bound to KRAS, however, and Craik, wondered whether they might make cancer cells more “visible” to the immune system.
“We suspected early on that the KRAS drugs might serve as permanent flags for cancer cells,” Craik said.
Harnessing Radiation for Precision Therapy
In 2022, a UCSF team that included Craik and Shokat demonstrated this was indeed possible.
The team designed an antibody that recognized the unique drug/KRAS surface fragment and beckoned to immune cells.
However, the approach needed the immune system to have the strength to beat the cancer by itself, which turned out not to be that effective.
Bringing Atomic-Level Radiation to Cancer Cells
Around the same time, Craik began working with Mike Evans, PhD, a professor of radiology at UCSF, to develop a different approach to destroy cancer cells.
They still used the K-RAS drug to flag cancerous cells, but this time they armed the antibodies with radioactive payloads.
The combination worked, eliminating lung cancer in mice with minimal side effects.
“Radiation is ruthlessly efficient in its ability to ablate cancer cells, and with this approach, we’ve shown that we can direct it exclusively to those cancers,” Evans said.
Added Craik, “The beauty of this approach is that we can calculate an extremely safe dose of radiation. Unlike external beam radiation, this method uses only the amount of radiation needed to beat the cancer.”
Customizing Treatment for More Patients
To make this therapy work in most patients, scientists will have to develop antibodies that account for the different ways that people’s cells display KRAS.
The UCSF team is now working on this – motivated by their own evidence that it can work.
Kliment Verba, PhD, an assistant professor of cellular and molecular pharmacology at UCSF, used cryo-electron microscopy to visualize the ‘radiation sandwich’ in atomic detail, giving the field a structure to develop even better antibodies.
“The drug bound to the KRAS peptide sticks out like a sore thumb, which the antibody then grabs,” said Verba, who like Craik is a member of UCSF’s Quantitative Biosciences Institute (QBI). “We’ve taken a significant step toward patient-specific radiation therapies, which could lead to a new paradigm for treatment.”
Reference: “Therapeutic Targeting and Structural Characterization of a Sotorasib-Modified KRAS G12C–MHC I Complex Demonstrate the Antitumor Efficacy of Hapten-Based Strategies” by Apurva Pandey, Peter J. Rohweder, Lieza M. Chan, Chayanid Ongpipattanakul, Dong hee Chung, Bryce Paolella, Fiona M. Quimby, Ngoc Nguyen, Kliment A. Verba, Michael J. Evans and Charles S. Craik, 15 January 2025, Cancer Research.
DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-24-2450
Authors: In addition to Craik, Evans, and Verba, other UCSF authors are Apurva Pandey, PhD, Peter J. Rohweder, PhD, Lieza M. Chan, Chayanid Ongpipattanakul, PhD, Dong hee Chung, PhD, Bryce Paolella, Fiona M. Quimby, Ngoc Nguyen, MS.
Funding and disclosures: This work was supported by the NIH (T32 GM 064337, P41-GM103393, S10OD020054, S10OD021741, and S10OD026881), the UCSF Innovation Ventures Philanthropy Fund, the UCSF Marcus Program in Precision Medicine, and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Craik, Evans, and Rohweder are inventors on a patent application covering part of this work and owned by UCSF. Craik, Ongpipattanakul, and Rohweder are inventors on a patent application related to this technology owned by UCSF. Craik and Rohweder are co-founders and shareholders of Hap10Bio and Evans and Paolella are shareholders of Hap10Bio.
News
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]
New book from NanoappsMedical Inc – Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
A Virus Designed in the Lab Could Help Defeat Antibiotic Resistance
Scientists can now design bacteria-killing viruses from DNA, opening a faster path to fighting superbugs. Bacteriophages have been used as treatments for bacterial infections for more than a century. Interest in these viruses is rising [...]
Sleep Deprivation Triggers a Strange Brain Cleanup
When you don’t sleep enough, your brain may clean itself at the exact moment you need it to think. Most people recognize the sensation. After a night of inadequate sleep, staying focused becomes harder [...]
Lab-grown corticospinal neurons offer new models for ALS and spinal injuries
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife as the final [...]
Urgent warning over deadly ‘brain swelling’ virus amid fears it could spread globally
Airports across Asia have been put on high alert after India confirmed two cases of the deadly Nipah virus in the state of West Bengal over the past month. Thailand, Nepal and Vietnam are among the [...]
This Vaccine Stops Bird Flu Before It Reaches the Lungs
A new nasal spray vaccine could stop bird flu at the door — blocking infection, reducing spread, and helping head off the next pandemic. Since first appearing in the United States in 2014, H5N1 [...]
These two viruses may become the next public health threats, scientists say
Two emerging pathogens with animal origins—influenza D virus and canine coronavirus—have so far been quietly flying under the radar, but researchers warn conditions are ripe for the viruses to spread more widely among humans. [...]
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells
COVID-19 viral fragments shown to target and kill specific immune cells in UCLA-led study Clues about extreme cases and omicron’s effects come from a cross-disciplinary international research team New research shows that after the [...]
Smaller Than a Grain of Salt: Engineers Create the World’s Tiniest Wireless Brain Implant
A salt-grain-sized neural implant can record and transmit brain activity wirelessly for extended periods. Researchers at Cornell University, working with collaborators, have created an extremely small neural implant that can sit on a grain of [...]
Scientists Develop a New Way To See Inside the Human Body Using 3D Color Imaging
A newly developed imaging method blends ultrasound and photoacoustics to capture both tissue structure and blood-vessel function in 3D. By blending two powerful imaging methods, researchers from Caltech and USC have developed a new way to [...]
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]