A new study led by the University of Kansas might resolve a mystery in the "aging process" in species — or, how a species' risk of going extinct changes after that species appears on the scene.
For years, evolutionary biologists believed older species lacked any real advantage over younger ones in avoiding extinction — an idea known as "Red Queen theory" among researchers.
Revisiting the Red Queen Theory
"The Red Queen theory is that species have to keep running just to stay still, like the character in Lewis Carroll's book 'Through the Looking-Glass,'" said lead author James Saulsbury, a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Ecology & Evolutionary Biology at KU. "This idea was turned into a kind of ecological theory in the 1970s in an attempt to explain an observation that extinction risk didn't seem to change over the lifespan of species."
Yet the years have not been kind to this theory.
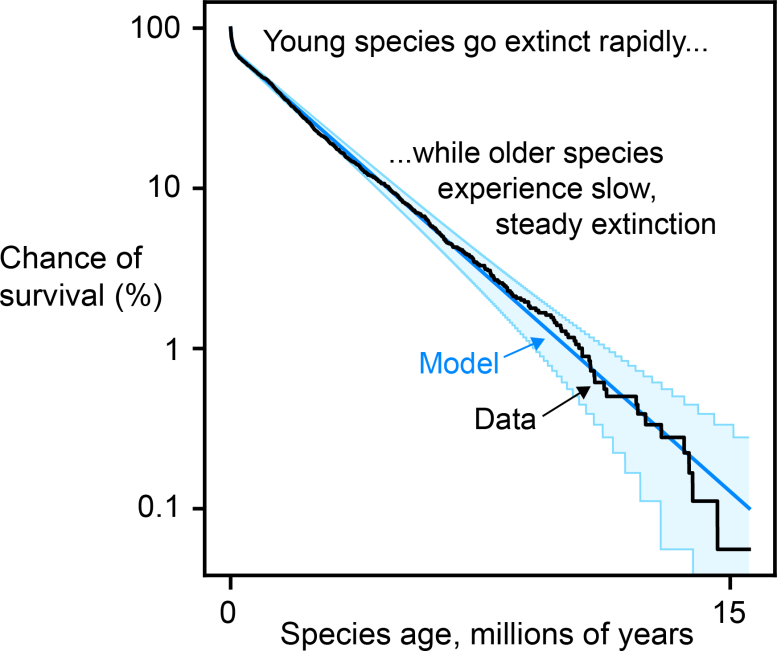
"In the earliest investigations of this phenomenon, species of all ages seemed to go extinct at about the same rate, perhaps just because of the relative crudeness of the evidence available at the time," Saulsbury said. "This made sense under this Red Queen model, where species are constantly competing with other species that are also adapting alongside them."
Questioning and Beyond the Red Queen
But as more data was collected and analyzed in more sophisticated ways, scientists increasingly found refutations of Red Queen theory.
Younger species are generally at greater risk of extinction. A new model from the University of Kansas shows this newer finding of age-dependent extinction while also emphasizing the importance of zero-sum competition in explaining extinction, as in the older Red Queen theory. Credit: Saulsbury et al
"Scientists kept finding instances where young species are especially at risk of extinction," Saulsbury said. "So we had a theory vacuum – a bunch of anomalous observations and no unified way of understanding them."
But now, Saulsbury has led research appearing in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences that may resolve this mystery. Saulsbury and his co-authors showed the relationship between a species' age and its risk of going extinct could be accurately predicted by an ecological model called the "neutral theory of biodiversity."
Neutral Theory's Insights
Neutral theory is a simple model of ecologically similar species competing for limited resources, where the outcome for each species is more or less random.
In the theory, "Species either go extinct or expand from small initial population size to become less vulnerable to extinction, but they are always susceptible to being replaced by their competitors," according to a lay summary of the PNAS paper. By extending this theory to make predictions for the fossil record, Saulsbury and colleagues found that neutral theory "predicts survivorship among fossil zooplankton with surprising accuracy and accounts for empirical deviations from the predictions of Red Queen more generally."
Saulsbury's co-authors were C. Tomomi Parins-Fukuchi of the University of Toronto, Connor Wilson of the University of Oxford and the University of Arizona, and Trond Reitan and Lee Hsiang Liow of the University of Oslo.
While neutral theory might seem to spell curtains for the Red Queen theory, the KU researcher said the Red Queen still has value. Mainly, it proposes the still valid idea that species compete in a zero-sum game against one another for finite resources, always battling for a bigger slice of nature's pie.
"Red Queen theory has been a compelling and important idea in the evolutionary biological community, but the data from the fossil record no longer seems to support that theory," Saulsbury said. "But I don't think our paper really refutes this idea because, in fact, the Red Queen theory and the neutral theory are, in a deep way, pretty similar. They both present a picture of extinction happening as a result of competition between species for resources and of constant turnover in communities resulting from biological interactions."
Relevance and Implications for Conservation
Ultimately, the findings not only help make sense of the forces that shape the natural world but may be relevant for conservation efforts as species face increasing threats from climate change and habitat loss around the globe.
"What makes a species vulnerable to extinction?" Saulsbury asked. "People are interested in learning from the fossil record whether it can tell us anything to help conserve species. The pessimistic side of our study is that there are ecological situations where there isn't a whole lot of predictability in the fates of species; there's some limit to how much we can predict extinction. To some extent, extinction will be decided by seemingly random forces — accidents of history. There's some support for this in paleobiological studies."
He said there has been effort to understand predictors of extinction in the fossil record, but not many generalities have emerged so far.
"There's no trait that makes you immortal or not susceptible to extinction," Saulsbury said. "But the optimistic side of our study is that entire communities can have patterns of extinction that are quite predictable and understandable. We can get a pretty good grasp on features of the biota, like how the extinction risk of species changes as they age. Even if the fate of a single species can be hard to predict, the fate of a whole community can be quite understandable."
Saulsbury added a caveat: It remains to be seen how broadly the neutral explanation for extinction succeeds across different parts of the tree of life.
"Our study is also working on the geological timescale in millions of years," he said. "Things may look very different on the timescale of our own lifetimes."
Reference: "Age-dependent extinction and the neutral theory of biodiversity" by James G. Saulsbury, C. Tomomi Parins-Fukuchi, Connor J. Wilson, Trond Reitan and Lee Hsiang Liow, 27 December 2023, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2307629121
News
Scientists Unlock a New Way to Hear the Brain’s Hidden Language
Scientists can finally hear the brain’s quietest messages—unlocking the hidden code behind how neurons think, decide, and remember. Scientists have created a new protein that can capture the incoming chemical signals received by brain [...]
Does being infected or vaccinated first influence COVID-19 immunity?
A new study analyzing the immune response to COVID-19 in a Catalan cohort of health workers sheds light on an important question: does it matter whether a person was first infected or first vaccinated? [...]
We May Never Know if AI Is Conscious, Says Cambridge Philosopher
As claims about conscious AI grow louder, a Cambridge philosopher argues that we lack the evidence to know whether machines can truly be conscious, let alone morally significant. A philosopher at the University of [...]
AI Helped Scientists Stop a Virus With One Tiny Change
Using AI, researchers identified one tiny molecular interaction that viruses need to infect cells. Disrupting it stopped the virus before infection could begin. Washington State University scientists have uncovered a method to interfere with a key [...]
Deadly Hospital Fungus May Finally Have a Weakness
A deadly, drug-resistant hospital fungus may finally have a weakness—and scientists think they’ve found it. Researchers have identified a genetic process that could open the door to new treatments for a dangerous fungal infection [...]
Fever-Proof Bird Flu Variant Could Fuel the Next Pandemic
Bird flu viruses present a significant risk to humans because they can continue replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever. Fever is one of the body’s main tools for slowing or stopping viral [...]
What could the future of nanoscience look like?
Society has a lot to thank for nanoscience. From improved health monitoring to reducing the size of electronics, scientists’ ability to delve deeper and better understand chemistry at the nanoscale has opened up numerous [...]
Scientists Melt Cancer’s Hidden “Power Hubs” and Stop Tumor Growth
Researchers discovered that in a rare kidney cancer, RNA builds droplet-like hubs that act as growth control centers inside tumor cells. By engineering a molecular switch to dissolve these hubs, they were able to halt cancer [...]
Platelet-inspired nanoparticles could improve treatment of inflammatory diseases
Scientists have developed platelet-inspired nanoparticles that deliver anti-inflammatory drugs directly to brain-computer interface implants, doubling their effectiveness. Scientists have found a way to improve the performance of brain-computer interface (BCI) electrodes by delivering anti-inflammatory drugs directly [...]
After 150 years, a new chapter in cancer therapy is finally beginning
For decades, researchers have been looking for ways to destroy cancer cells in a targeted manner without further weakening the body. But for many patients whose immune system is severely impaired by chemotherapy or radiation, [...]
Older chemical libraries show promise for fighting resistant strains of COVID-19 virus
SARS‑CoV‑2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to mutate, with some newer strains becoming less responsive to current antiviral treatments like Paxlovid. Now, University of California San Diego scientists and an international team of [...]
Lower doses of immunotherapy for skin cancer give better results, study suggests
According to a new study, lower doses of approved immunotherapy for malignant melanoma can give better results against tumors, while reducing side effects. This is reported by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in the Journal of the National [...]
Researchers highlight five pathways through which microplastics can harm the brain
Microplastics could be fueling neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, with a new study highlighting five ways microplastics can trigger inflammation and damage in the brain. More than 57 million people live with dementia, [...]
Tiny Metal Nanodots Obliterate Cancer Cells While Largely Sparing Healthy Tissue
Scientists have developed tiny metal-oxide particles that push cancer cells past their stress limits while sparing healthy tissue. An international team led by RMIT University has developed tiny particles called nanodots, crafted from a metallic compound, [...]
Gold Nanoclusters Could Supercharge Quantum Computers
Researchers found that gold “super atoms” can behave like the atoms in top-tier quantum systems—only far easier to scale. These tiny clusters can be customized at the molecular level, offering a powerful, tunable foundation [...]
A single shot of HPV vaccine may be enough to fight cervical cancer, study finds
WASHINGTON -- A single HPV vaccination appears just as effective as two doses at preventing the viral infection that causes cervical cancer, researchers reported Wednesday. HPV, or human papillomavirus, is very common and spread [...]