Recent estimates indicate that deadly antibiotic-resistant infections will rapidly escalate over the next quarter century. More than 1 million people died from drug-resistant infections each year from 1990 to 2021, a recent study reported, with new projections surging to nearly 2 million deaths each year by 2050.
In an effort to counteract this public health crisis, scientists are looking for new solutions inside the intricate mechanics of bacterial infection. A study led by researchers at the University of California San Diego has discovered a vulnerability within strains of bacteria that are antibiotic resistant.
Working with labs at Arizona State University and the Universitat Pompeu Fabra (Spain), Professor Gürol Süel and colleagues in UC San Diego’s School of Biological Sciences investigated the antibiotic resistance of the bacterium Bacillus subtilis.
Their research was motivated by the question of why mutant variants of bacteria do not proliferate and take over the population once they have developed an antibiotic-resistant advantage. With an upper hand over other bacteria lacking similar antibiotic resistance, such bacteria should become dominant. Yet they are not. Why?
The answer, reported in the journal Science Advances, is that antibiotic resistance comes at a cost. While antibiotic resistance provides some advantages for the bacteria to survive, the team discovered that it’s also linked with a physiological limitation that hinders potential dominance.
This fact, the researchers note, potentially could be exploited to stop the spread of antibiotic resistance.
“We discovered an Achilles heel of antibiotic resistant bacteria,” said Süel, a member of the Department of Molecular Biology at UC San Diego. “We can take advantage of this cost to suppress the establishment of antibiotic resistance without drugs or harmful chemicals.”
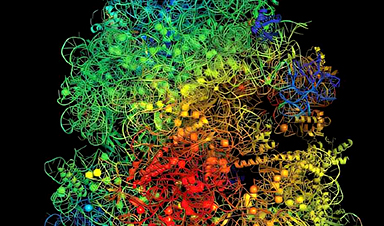
Spontaneous mutations of DNA arise in all living cells, including those within bacteria. Some of these mutations lead to antibiotic resistance. Süel and his colleagues focused on physiological mechanisms related to ribosomes, the micro machines within cells that play a key role in synthesizing proteins and translating genetic codes.

Credit: Ashley Moon, Süel Lab, UC San Diego
All cells rely on charged ions such as magnesium ions to survive. Ribosomes are dependent upon magnesium ions since this metal cation helps stabilize their structure and function.
However, atomic-scale modeling during the new research found that mutant ribosome variants that bestow antibiotic resistance excessively compete for magnesium ions with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules, which provide energy to drive living cells. Mathematical models further showed that this results in a ribosome versus ATP tug-of-war over a limited supply of magnesium in the cell.
Studying a ribosome variant within Bacillus subtilis called “L22,” the researchers found that competition for magnesium hinders the growth of L22 more than a normal “wild type” ribosome that is not resistant to antibiotics. Hence, the competition levies a physiological toll linked to mutant bacteria with resistance.
“While we often think of antibiotic resistance as a major benefit for bacteria to survive, we found that the ability to cope with magnesium limitation in their environment is more important for bacterial proliferation,” said Süel.
This newly discovered weakness can now be used as a target to counteract antibiotic resistance without the use of drugs or toxic chemicals. For example, it may be possible to chelate magnesium ions from bacterial environments, which should selectively inhibit resistant strains without impacting the wild type bacteria that may be beneficial to our health.
“We show that through a better understanding of the molecular and physiological properties of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, we can find novel ways to control them without the use of drugs,” said Süel.
In October, Süel and colleagues at the University of Chicago announced a separate approach to combating the antibacterial-resistant bacteria health crisis. Their development of a bioelectronic device that taps into the natural electrical activity of certain bacteria found on our skin paves the way for another drug-free approach to managing infections.
The advancement was proven to reduce the harmful effects of Staphylococcus epidermidis, a common bacterium known for causing hospital-acquired infections and contributing to antibiotic resistance. In both studies, the researchers used charged ions to control bacteria.
“We are running out of effective antibiotics and their rampant use over the decades has resulted in antibiotics being spread across the globe, from the arctic to the oceans and our groundwater,” said Süel. “Drug-free alternatives to treating bacterial infections are needed and our two most recent studies show how we can indeed achieve drug-free control over antibiotic resistant bacteria.”
The authors of the new study were: Eun Chae Moon, Tushar Modi, Dong-yeon Lee, Danis Yangaliev, Jordi Garcia-Ojalvo, S. Banu Ozkan and Gürol Süel.
More information: Eun Chae Moon et al, Physiological cost of antibiotic resistance: Insights from a ribosome variant in bacteria, Science Advances (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adq5249. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adq5249
Journal information: Science Advances
News
Differentiating cancerous and healthy cells through motion analysis
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have found that the motion of unlabeled cells can be used to tell whether they are cancerous or healthy. They observed malignant fibrosarcoma cells and [...]
This Tiny Cellular Gate Could Be the Key to Curing Cancer – And Regrowing Hair
After more than five decades of mystery, scientists have finally unveiled the detailed structure and function of a long-theorized molecular machine in our mitochondria — the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier. This microscopic gatekeeper controls how [...]
Unlocking Vision’s Secrets: Researchers Reveal 3D Structure of Key Eye Protein
Researchers have uncovered the 3D structure of RBP3, a key protein in vision, revealing how it transports retinoids and fatty acids and how its dysfunction may lead to retinal diseases. Proteins play a critical [...]
5 Key Facts About Nanoplastics and How They Affect the Human Body
Nanoplastics are typically defined as plastic particles smaller than 1000 nanometers. These particles are increasingly being detected in human tissues: they can bypass biological barriers, accumulate in organs, and may influence health in ways [...]
Measles Is Back: Doctors Warn of Dangerous Surge Across the U.S.
Parents are encouraged to contact their pediatrician if their child has been exposed to measles or is showing symptoms. Pediatric infectious disease experts are emphasizing the critical importance of measles vaccination, as the highly [...]
AI at the Speed of Light: How Silicon Photonics Are Reinventing Hardware
A cutting-edge AI acceleration platform powered by light rather than electricity could revolutionize how AI is trained and deployed. Using photonic integrated circuits made from advanced III-V semiconductors, researchers have developed a system that vastly [...]
A Grain of Brain, 523 Million Synapses, Most Complicated Neuroscience Experiment Ever Attempted
A team of over 150 scientists has achieved what once seemed impossible: a complete wiring and activity map of a tiny section of a mammalian brain. This feat, part of the MICrONS Project, rivals [...]
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area of key focus for the [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is actually broken down into carbon [...]
How Everyday Plastics Quietly Turn Into DNA-Damaging Nanoparticles
The same unique structure that makes plastic so versatile also makes it susceptible to breaking down into harmful micro- and nanoscale particles. The world is saturated with trillions of microscopic and nanoscopic plastic particles, some smaller [...]
AI Outperforms Physicians in Real-World Urgent Care Decisions, Study Finds
The study, conducted at the virtual urgent care clinic Cedars-Sinai Connect in LA, compared recommendations given in about 500 visits of adult patients with relatively common symptoms – respiratory, urinary, eye, vaginal and dental. [...]
Challenging the Big Bang: A Multi-Singularity Origin for the Universe
In a study published in the journal Classical and Quantum Gravity, Dr. Richard Lieu, a physics professor at The University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH), which is a part of The University of Alabama System, suggests that [...]
New drug restores vision by regenerating retinal nerves
Vision is one of the most crucial human senses, yet over 300 million people worldwide are at risk of vision loss due to various retinal diseases. While recent advancements in retinal disease treatments have [...]
Shingles vaccine cuts dementia risk by 20%, new study shows
A shingles shot may do more than prevent rash — it could help shield the aging brain from dementia, according to a landmark study using real-world data from the UK. A routine vaccine could [...]
AI Predicts Sudden Cardiac Arrest Days Before It Strikes
AI can now predict deadly heart arrhythmias up to two weeks in advance, potentially transforming cardiac care. Artificial intelligence could play a key role in preventing many cases of sudden cardiac death, according to [...]