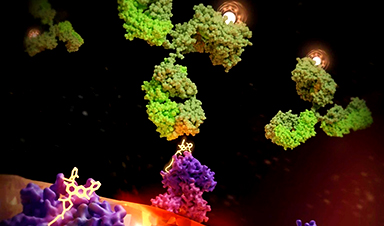
| The key to maximizing traditional or quantum computing speeds lies in our ability to understand how electrons behave in solids, and a collaboration between the University of Michigan and the University of Regensburg captured electron movement in attoseconds—the fastest speed yet. | |
| Seeing electrons move in increments of one quintillionth of a second could help push processing speeds up to a billion times faster than what is currently possible. In addition, the research offers a “game-changing” tool for the study of many-body physics. | |
| “Your current computer’s processor operates in gigahertz, that’s one billionth of a second per operation,” said Mackillo Kira, U-M professor of electrical engineering and computer science, who led the theoretical aspects of the study published in Nature (“Attosecond clocking of correlations between Bloch electrons”). “In quantum computing, that’s extremely slow because electrons within a computer chip collide trillions of times a second and each collision terminates the quantum computing cycle. |
| “What we’ve needed, in order to push performance forward, are snapshots of that electron movement that are a billion times faster. And now we have it.” | |
| Rupert Huber, professor of physics at the University of Regensburg and corresponding author of the study, said the result’s potential impact in the field of many-body physics could surpass its computing impact. | |
| “Many-body interactions are the microscopic driving forces behind the most coveted properties of solids—ranging from optical and electronic feats to intriguing phase transitions—but they have been notoriously difficult to access,” said Huber, who led the experiment. “Our solid-state attoclock could become a real game changer, allowing us to design novel quantum materials with more precisely tailored properties and help develop new materials platforms for future quantum information technology.” | |
| To see electron movement within two-dimensional quantum materials, researchers typically use short bursts of focused extreme ultraviolet (XUV) light. Those bursts can reveal the activity of electrons attached to an atom’s nucleus. But the large amounts of energy carried in those bursts prevent clear observation of the electrons that travel through semiconductors—as in current computers and in materials under exploration for quantum computers. | |
| U-M engineers and partners employ two light pulses with energy scales that match that of those movable semiconductor electrons. The first, a pulse of infrared light, puts the electrons into a state that allows them to travel through the material. The second, a lower-energy terahertz pulse, then forces those electrons into controlled head-on collision trajectories. The crashes produce bursts of light, the precise timing of which reveals interactions behind quantum information and exotic quantum materials alike. | |
| “We used two pulses—one that is energetically matched with the state of the electron, and then a second pulse that causes the state to change,” Kira said. “We can essentially film how these two pulses change the electron’s quantum state and then express that as a function of time.” | |
| The two-pulse sequence allows time measurement with a precision better than one percent of the oscillation period of the terahertz radiation that accelerates the electrons. | |
| “This is really unique and took us many years of development,” Huber said. “It is quite unexpected that such high-precision measurements are even possible if you remember how ridiculously short a single oscillation cycle of light is—and our time resolution is one hundred times faster yet.” | |
| Quantum materials could possess robust magnetic, superconductive or superfluid phases, and quantum computing represents the potential for solving problems that would take too long on classical computers. Pushing such quantum capabilities will eventually create solutions to problems that are currently out of our reach. That starts with basic observational science. | |
| “No one has been able to build a scalable and fault-tolerant quantum computer so far and we don’t even know what that would look like,” said study co-first author Markus Borsch, U-M doctoral student in electrical and computer engineering. “But basic research like studying how electronic motion in solids works on the most fundamental levels might give us an idea that leads us in the right direction.” |
News
Scientists Just Discovered an RNA That Repairs DNA Damage – And It’s a Game-Changer
Our DNA is constantly under threat — from cell division errors to external factors like sunlight and smoking. Fortunately, cells have intricate repair mechanisms to counteract this damage. Scientists have uncovered a surprising role played by [...]
What Scientists Just Discovered About COVID-19’s Hidden Death Toll
COVID-19 didn’t just claim lives directly—it reshaped mortality patterns worldwide. A major international study found that life expectancy plummeted across most of the 24 analyzed countries, with additional deaths from cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, and mental [...]
Self-Propelled Nanoparticles Improve Immunotherapy for Non-Invasive Bladder Cancer
A study led by Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) and the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) in South Korea details the creation of urea-powered nanomotors that enhance immunotherapy for bladder cancer. The nanomotors [...]
Scientists Develop New System That Produces Drinking Water From Thin Air
UT Austin researchers have developed a biodegradable, biomass-based hydrogel that efficiently extracts drinkable water from the air, offering a scalable, sustainable solution for water access in off-grid communities, emergency relief, and agriculture. Discarded food [...]
AI Unveils Hidden Nanoparticles – A Breakthrough in Early Disease Detection
Deep Nanometry (DNM) is an innovative technique combining high-speed optical detection with AI-driven noise reduction, allowing researchers to find rare nanoparticles like extracellular vesicles (EVs). Since EVs play a role in disease detection, DNM [...]
Inhalable nanoparticles could help treat chronic lung disease
Nanoparticles designed to release antibiotics deep inside the lungs reduced inflammation and improved lung function in mice with symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By Grace Wade Delivering medication to the lungs with inhalable nanoparticles [...]
New MRI Study Uncovers Hidden Lung Abnormalities in Children With Long COVID
Long COVID is more than just lingering symptoms—it may have a hidden biological basis that standard medical tests fail to detect. A groundbreaking study using advanced MRI technology has uncovered significant lung abnormalities in [...]
AI Struggles with Abstract Thought: Study Reveals GPT-4’s Limits
While GPT-4 performs well in structured reasoning tasks, a new study shows that its ability to adapt to variations is weak—suggesting AI still lacks true abstract understanding and flexibility in decision-making. Artificial Intelligence (AI), [...]
Turning Off Nerve Signals: Scientists Develop Promising New Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
Pancreatic cancer reprograms nerve cells to fuel its growth, but blocking these connections can shrink tumors and boost treatment effectiveness. Pancreatic cancer is closely linked to the nervous system, according to researchers from the [...]
New human antibody shows promise for Ebola virus treatment
New research led by scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) reveals the workings of a human antibody called mAb 3A6, which may prove to be an important component for Ebola virus therapeutics. [...]
Early Alzheimer’s Detection Test – Years Before Symptoms Appear
A new biomarker test can detect early-stage tau protein clumping up to a decade before it appears on brain scans, improving early Alzheimer’s diagnosis. Unlike amyloid-beta, tau neurofibrillary tangles are directly linked to cognitive decline. Years [...]
New mpox variant can spread rapidly across borders
International researchers, including from DTU National Food Institute, warn that the ongoing mpox outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has the potential to spread across borders more rapidly. The mpox virus [...]
How far would you trust AI to make important decisions?
From tailored Netflix recommendations to personalized Facebook feeds, artificial intelligence (AI) adeptly serves content that matches our preferences and past behaviors. But while a restaurant tip or two is handy, how comfortable would you [...]
Can AI Really Think? Research Reveals Gaps in Logical Execution
While AI models can break down problems into structured steps, new research reveals they still fail at basic arithmetic and fact-checking—raising questions about their true reasoning abilities. Large Language Models (LLMs) have become indispensable [...]
Scientists Just Made Cancer Radiation Therapy Smarter, Safer, and More Precise
Scientists at UC San Francisco have developed a revolutionary cancer treatment that precisely targets tumors with radiation while sparing healthy tissues. By using a KRAS-targeting drug to mark cancer cells and attaching a radioactive [...]
Superbugs Are Losing to Science, Light, and a Little Spice
Texas A&M researchers have found that curcumin, when activated by light, can weaken antibiotic-resistant bacteria, restoring the effectiveness of conventional antibiotics. Curcumin: A Surprising Ally Against Superbugs In 2017, a woman admitted to a [...]