This major scientific advance has implications for many fields, including energy-efficient computers and quantum technology.
Until recently, physicists widely believed that it was impossible to compress light below the so-called diffraction limit, except when utilizing metal nanoparticles, which also absorb light. As a result, it seemed to be impossible to compress light strongly in dielectric materials like silicon, which are essential for information technologies and had the significant advantage of not absorbing light. Interestingly, it was theoretically shown that the diffraction limit does not apply to dielectrics back in 2006. However, no one has been able to demonstrate this in the actual world due to the fact that it requires such complex nanotechnology that no one has yet been able to create the required dielectric nanostructures.
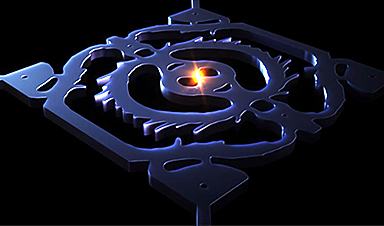
A research team from the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) has created a device known as a "dielectric nanocavity" that successfully concentrates light in a volume 12 times smaller than the diffraction limit. The finding is groundbreaking in optical research and was recently published in the journal Nature Communications.
"Although computer calculations show that you can concentrate light at an infinitely small point, this only applies in theory. The actual results are limited by how small details can be made, for example, on a microchip," says Marcus Albrechtsen, Ph.D.-student at DTU Electro and the first author of the new article.
Optical nanocavities are structures that have been specially designed to retain light so that it does not travel normally but is tossed back and forth as if two mirrors were facing each other. The closer the mirrors are to one other, the more intense the light between them gets. For this experiment, the researchers created a bowtie structure, which is particularly effective in squeezing photons together due to its unique shape.
The diffraction limit
The theory of the diffraction limit describes that light cannot be focused to a volume smaller than half the wavelength in an optical system – for example, this applies to the resolution in microscopes.
However, nanostructures can consist of elements much smaller than the wavelength, which means that the diffraction limit is no longer a fundamental limit. Bowtie structures, in particular, can compress the light into very small volumes limited by the sizes of the bowtie and, thus, the quality of the nanofabrication.
When the light is compressed, it becomes more intense, enhancing interactions between light and materials such as atoms, molecules, and 2D materials.
Dielectric materials
Dielectric materials are electrically insulating. Glass, rubber, and plastic are examples of dielectric materials, and they contrast with metals, which are electrically conductive.
An example of a dielectric material is silicon, which is often used in electronics but also in photonics.
Interdisciplinary efforts and excellent methods
The nanocavity is made of silicon, the dielectric material on which most advanced modern technology is based. The material for the nanocavity was developed in cleanroom laboratories at DTU, and the patterns on which the cavity is based are optimized and designed using a unique method for topology optimization developed at DTU. Initially developed to design bridges and aircraft wings, it is now also used for nanophotonic structures.
"It required a great joint effort to achieve this breakthrough. It has only been possible because we have managed to combine world-leading research from several research groups at DTU," says associate professor Søren Stobbe, who has led the research work."
Important breakthrough for energy-efficient technology
The discovery could be decisive for developing revolutionary new technologies that may reduce the amount of energy-guzzling components in data centers, computers, telephones, etc.
The energy consumption for computers and data centers continues to grow, and there is a need for more sustainable chip architectures that use less energy. This can be achieved by replacing electrical circuits with optical components. The researchers' vision is to use the same division of labor between light and electrons used for the Internet, where light is used for communication and electronics for data processing. The only difference is that both functionalities must be built into the same chip, which requires that the light be compressed to the same size as the electronic components. The breakthrough at DTU shows that it is, in fact, possible.
"There is no doubt that this is an important step to developing a more energy-efficient technology for, e.g., nanolasers for optical connections in data centers and future computers – but there is still a long way to go," says Marcus Albrechtsen.
The researchers will now work further and refine methods and materials to find the optimal solution.
"Now that we have the theory and method in place, we will be able to make increasingly intense photons as the surrounding technology develops. I am convinced that this is just the first of a long series of major developments in physics and photonic nanotechnology centered around these principles," says Søren Stobbe, who recently received the prestigious Consolidator Grant from the European Research Council of € 2 million for the development of a completely new type of light source based on the new cavities.
News
Fever-Proof Bird Flu Variant Could Fuel the Next Pandemic
Bird flu viruses present a significant risk to humans because they can continue replicating at temperatures higher than a typical fever. Fever is one of the body’s main tools for slowing or stopping viral [...]
What could the future of nanoscience look like?
Society has a lot to thank for nanoscience. From improved health monitoring to reducing the size of electronics, scientists’ ability to delve deeper and better understand chemistry at the nanoscale has opened up numerous [...]
Scientists Melt Cancer’s Hidden “Power Hubs” and Stop Tumor Growth
Researchers discovered that in a rare kidney cancer, RNA builds droplet-like hubs that act as growth control centers inside tumor cells. By engineering a molecular switch to dissolve these hubs, they were able to halt cancer [...]
Platelet-inspired nanoparticles could improve treatment of inflammatory diseases
Scientists have developed platelet-inspired nanoparticles that deliver anti-inflammatory drugs directly to brain-computer interface implants, doubling their effectiveness. Scientists have found a way to improve the performance of brain-computer interface (BCI) electrodes by delivering anti-inflammatory drugs directly [...]
After 150 years, a new chapter in cancer therapy is finally beginning
For decades, researchers have been looking for ways to destroy cancer cells in a targeted manner without further weakening the body. But for many patients whose immune system is severely impaired by chemotherapy or radiation, [...]
Older chemical libraries show promise for fighting resistant strains of COVID-19 virus
SARS‑CoV‑2, the virus that causes COVID-19, continues to mutate, with some newer strains becoming less responsive to current antiviral treatments like Paxlovid. Now, University of California San Diego scientists and an international team of [...]
Lower doses of immunotherapy for skin cancer give better results, study suggests
According to a new study, lower doses of approved immunotherapy for malignant melanoma can give better results against tumors, while reducing side effects. This is reported by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in the Journal of the National [...]
Researchers highlight five pathways through which microplastics can harm the brain
Microplastics could be fueling neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, with a new study highlighting five ways microplastics can trigger inflammation and damage in the brain. More than 57 million people live with dementia, [...]
Tiny Metal Nanodots Obliterate Cancer Cells While Largely Sparing Healthy Tissue
Scientists have developed tiny metal-oxide particles that push cancer cells past their stress limits while sparing healthy tissue. An international team led by RMIT University has developed tiny particles called nanodots, crafted from a metallic compound, [...]
Gold Nanoclusters Could Supercharge Quantum Computers
Researchers found that gold “super atoms” can behave like the atoms in top-tier quantum systems—only far easier to scale. These tiny clusters can be customized at the molecular level, offering a powerful, tunable foundation [...]
A single shot of HPV vaccine may be enough to fight cervical cancer, study finds
WASHINGTON -- A single HPV vaccination appears just as effective as two doses at preventing the viral infection that causes cervical cancer, researchers reported Wednesday. HPV, or human papillomavirus, is very common and spread [...]
New technique overcomes technological barrier in 3D brain imaging
Scientists at the Swiss Light Source SLS have succeeded in mapping a piece of brain tissue in 3D at unprecedented resolution using X-rays, non-destructively. The breakthrough overcomes a long-standing technological barrier that had limited [...]
Scientists Uncover Hidden Blood Pattern in Long COVID
Researchers found persistent microclot and NET structures in Long COVID blood that may explain long-lasting symptoms. Researchers examining Long COVID have identified a structural connection between circulating microclots and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). The [...]
This Cellular Trick Helps Cancer Spread, but Could Also Stop It
Groups of normal cbiells can sense far into their surroundings, helping explain cancer cell migration. Understanding this ability could lead to new ways to limit tumor spread. The tale of the princess and the [...]
New mRNA therapy targets drug-resistant pneumonia
Bacteria that multiply on surfaces are a major headache in health care when they gain a foothold on, for example, implants or in catheters. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden have found [...]
Current Heart Health Guidelines Are Failing To Catch a Deadly Genetic Killer
New research reveals that standard screening misses most people with a common inherited cholesterol disorder. A Mayo Clinic study reports that current genetic screening guidelines overlook most people who have familial hypercholesterolemia, an inherited disorder that [...]