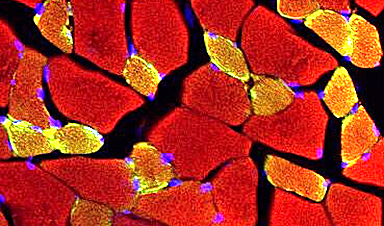
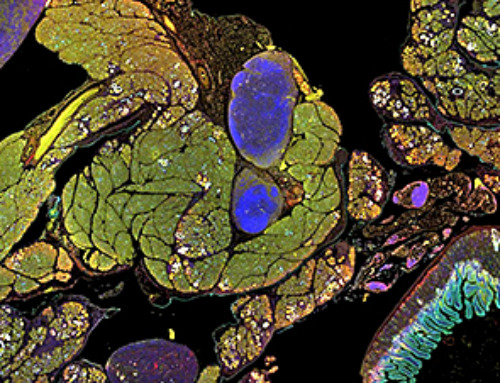
Cancer is a complex systemic disease, with accompanying secondary effects that can result in debilitating effects on the human body. Cancer-associated skeletal muscle weakening or loss, also called “cancer cachexia,” is a prevalent and serious condition responsible for 20%–30% of the deaths in affected cancer patients. In current treatments for cancer cachexia, there are limitations in efficacy levels and significant side effects.
Published in Molecular Therapy, the study found that drug-loaded RBCEVs inhibited target genes could increase muscle growth and suppress cancer cachexia. Compared to the delivery of a single RNA drug, muscle growth was observed to be further enhanced when two RNA drugs targeting two different genes implicated in cancer cachexia were loaded into the same RBCEVs. Importantly, repeated administrations with RBCEVs did not induce toxicity or inflammatory reactions, which is a prerequisite for clinical trials on humans.
“There is a lot of potential in using RNA-based drugs for conditions that are difficult to treat, but the delivery has always been tricky. From our previous and current studies, we have found that the RBCEV delivery platform can help to overcome some of the long-standing technical challenges in the field,” said Assistant Professor Minh Le from WisDM and the Department of Pharmacology at NUS Medicine, who led the study.
Professor Ng Shyh-Chang, Principal Investigator for the State Key Laboratory of Stem Cell and Reproductive Biology at the CAS Institute of Zoology, who co-directed the study, added, “Building on previous target discovery work, this is one of the first studies to leverage RNA therapies to treat cancer cachexia. This could lead to the use EV-based gene therapies to address unmet needs in cachexia and sarcopenia.”
The team has plans for further collaborations to test the use of RBCEV-delivered therapeutics against other targets in the muscles. At the same time, they have been working on applying RBCEVs to the treatment of different cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and COVID-19. Accumulating data from their studies, the RBCEV has shown to be a robust, safe and versatile platform.
As the collective understanding of RBCEV biology and related technologies continue to mature, the RBCEV platform is well-positioned for clinical translation to provide safer and more efficacious treatment options for muscle degenerative conditions as well as other challenging diseases.
News
Studies detail high rates of long COVID among healthcare, dental workers
Researchers have estimated approximately 8% of Americas have ever experienced long COVID, or lasting symptoms, following an acute COVID-19 infection. Now two recent international studies suggest that the percentage is much higher among healthcare workers [...]
Melting Arctic Ice May Unleash Ancient Deadly Diseases, Scientists Warn
Melting Arctic ice increases human and animal interactions, raising the risk of infectious disease spread. Researchers urge early intervention and surveillance. Climate change is opening new pathways for the spread of infectious diseases such [...]
Scientists May Have Found a Secret Weapon To Stop Pancreatic Cancer Before It Starts
Researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory have found that blocking the FGFR2 and EGFR genes can stop early-stage pancreatic cancer from progressing, offering a promising path toward prevention. Pancreatic cancer is expected to become [...]
Breakthrough Drug Restores Vision: Researchers Successfully Reverse Retinal Damage
Blocking the PROX1 protein allowed KAIST researchers to regenerate damaged retinas and restore vision in mice. Vision is one of the most important human senses, yet more than 300 million people around the world are at [...]
Differentiating cancerous and healthy cells through motion analysis
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have found that the motion of unlabeled cells can be used to tell whether they are cancerous or healthy. They observed malignant fibrosarcoma cells and [...]
This Tiny Cellular Gate Could Be the Key to Curing Cancer – And Regrowing Hair
After more than five decades of mystery, scientists have finally unveiled the detailed structure and function of a long-theorized molecular machine in our mitochondria — the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier. This microscopic gatekeeper controls how [...]
Unlocking Vision’s Secrets: Researchers Reveal 3D Structure of Key Eye Protein
Researchers have uncovered the 3D structure of RBP3, a key protein in vision, revealing how it transports retinoids and fatty acids and how its dysfunction may lead to retinal diseases. Proteins play a critical [...]
5 Key Facts About Nanoplastics and How They Affect the Human Body
Nanoplastics are typically defined as plastic particles smaller than 1000 nanometers. These particles are increasingly being detected in human tissues: they can bypass biological barriers, accumulate in organs, and may influence health in ways [...]
Measles Is Back: Doctors Warn of Dangerous Surge Across the U.S.
Parents are encouraged to contact their pediatrician if their child has been exposed to measles or is showing symptoms. Pediatric infectious disease experts are emphasizing the critical importance of measles vaccination, as the highly [...]
AI at the Speed of Light: How Silicon Photonics Are Reinventing Hardware
A cutting-edge AI acceleration platform powered by light rather than electricity could revolutionize how AI is trained and deployed. Using photonic integrated circuits made from advanced III-V semiconductors, researchers have developed a system that vastly [...]
A Grain of Brain, 523 Million Synapses, Most Complicated Neuroscience Experiment Ever Attempted
A team of over 150 scientists has achieved what once seemed impossible: a complete wiring and activity map of a tiny section of a mammalian brain. This feat, part of the MICrONS Project, rivals [...]
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area of key focus for the [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is actually broken down into carbon [...]
How Everyday Plastics Quietly Turn Into DNA-Damaging Nanoparticles
The same unique structure that makes plastic so versatile also makes it susceptible to breaking down into harmful micro- and nanoscale particles. The world is saturated with trillions of microscopic and nanoscopic plastic particles, some smaller [...]
AI Outperforms Physicians in Real-World Urgent Care Decisions, Study Finds
The study, conducted at the virtual urgent care clinic Cedars-Sinai Connect in LA, compared recommendations given in about 500 visits of adult patients with relatively common symptoms – respiratory, urinary, eye, vaginal and dental. [...]