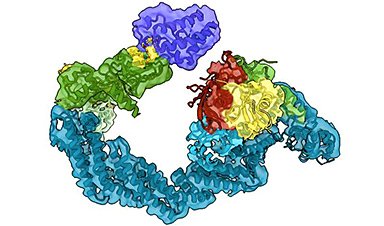
Researchers at the University of Dundee have revealed in the greatest detail yet the workings of molecules called protein degraders which can be deployed to combat what have previously been regarded as “undruggable” diseases, including cancers and neurodegenerative diseases.
Protein degrader molecules are heralding a revolution in drug discovery, with more than 50 drugs of this type currently being tested in clinical trials for patients with diseases for which no other options exist.
The Centre for Targeted Protein Degradation (CeTPD) at the University of Dundee is one of the world’s leading centers for research into how protein degraders work and how they can most effectively be put to use for a new generation of drugs.
Now researchers have revealed previously invisible levels of detail and understanding of how the protein degraders work, which in turn is allowing for even more targeted use of them at the molecular level.
Ph.D. student Charlotte Crowe, together with Dr. Mark Nakasone, Senior Postdoctoral Scientist at CeTPD, used a technique called cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), which enables scientists to see how biomolecules move and interact with each other.
This works by flash-freezing proteins and using a focused electron beam and a high-resolution camera to generate millions of 2D images of the protein. They then used sophisticated software and artificial intelligence (AI) models which allowed them to generate 3D snapshots of the degrader drugs working in action.
Their latest research is published in the journal Science Advances and is expected to constitute a landmark contribution to research in the field of TPD and ubiquitin mechanisms.
“We have reached a level of detail where we can see how these protein degraders work and can be deployed [to recruit the disease-causing protein ] and target the ‘bull’s eye,’ in molecular terms,” said Charlotte Crowe, who carried out the research together with a wider team of Dundee researchers.
“Protein degrader molecules work in a way that is fundamentally different from the way conventional drugs work. However, until recently the exact details of how this process works at the molecular level had remained elusive.
“Proteins are typically a few nanometers large, which is 1 billionth of a meter, or 1 millionth of the width of a hair. So being able to ‘see’ them in action has not been possible, up until now.
“We have now been able to build a moving image of how it all happens, which means we can more specifically control the process with an incredible level of detail.”
Professor Alessio Ciulli, Director of CeTPD, said, “This is incredibly exciting work and opens up the possibility of even more effectively targeted drugs able to finally treat some diseases which up until now have been too difficult to tackle.”
How it works
Proteins are essential for our cells to function properly, but when these do not work correctly they can cause disease.
Targeted protein degradation involves redirecting protein recycling systems in our cells to destroy the disease-causing proteins. Protein degraders work by capturing the disease-causing protein and making it stick like a glue to the cellular protein-recycling machinery, which then tags the protein as expired in order to destroy it.
The tag is a small protein called ubiquitin, which effectively gets fired at the disease-causing protein like a bullet. In order for the process to work effectively, ubiquitin must hit the right spots on the target protein so that it gets tagged effectively. The new work by the Dundee team enables them to see how the bullet hits the proverbial bull’s eye.
Working with a protein degrader molecule called MZ1, which was developed in the Ciulli laboratory at Dundee, and using high-end mass spectrometry, they were able to identify exactly where on the target protein the vital “tags” are added.
The work shows how degrader drugs hold onto and position disease-causing proteins, making them good targets for receiving ubiquitin molecules (i.e., “ubiquitin-atable”) which then leads to their destruction inside the cell.
Protein degradation efficiency and productivity is dependent on the degrader molecule’s ability to hold tight onto the disease-causing protein, and in a position where it can most effectively act. This latest research paints a bull’s eye and holds it steady enough for the molecule to be accurately targeted.
Professor Ciulli said this and other recently published papers were contributing to rapid development of an exciting field of science and drug discovery. “This rapidly expanding field is fascinating and complementary articles on how this cellular protein-recycling machinery works to fire ubiquitin molecules at target proteins were recently published by the laboratories of biochemists Brenda Schulman (Max-Planck Institute of Biochemistry) and Gary Kleiger (University of Nevada, Las Vegas).
“Our collective work provides a leap forward in understanding that will accelerate development of new TPD drugs in future.”
This work comes from a local collaboration between two groups of scientists at the University of Dundee.
In the Centre for Targeted Protein Degradation, led by Professor Alessio Ciulli, were Charlotte Crowe, Mark Nakasone, Conner Craigon, Gajanan Sathe and Nikolai Makukhin. They worked with Professor Ron Hay, an expert in ubiquitin, based in the School of Life Sciences, and colleagues Sarah Chandler and Mike Tatham.
More information: Charlotte Crowe et al, Mechanism of degrader-targeted protein ubiquitinability, Science Advances (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ado6492. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.ado6492
Journal information: Science Advances
Provided by University of Dundee
News
Beneficial genetic changes observed in regular blood donors
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have identified genetic changes in blood stem cells from frequent blood donors that support the production of new, non-cancerous cells. Understanding the differences in the mutations that accumulate [...]
Shocking Amounts of Microplastics in the Brain – It Could Be Increasing Our Risk of Dementia
The brain has higher concentrations of plastic particles compared to other organs, with increased levels found in dementia patients. In a comprehensive commentary published in Brain Medicine, researchers highlight alarming new evidence of microplastic accumulation [...]
Baffling Scientists for Centuries: New Study Unravels Mystery of Static Electricity
ISTA physicists demonstrate that contact electrification depends on the contact history of materials. For centuries, static electricity has intrigued and perplexed scientists. Now, researchers from the Waitukaitis group at the Institute of Science and [...]
Tumor “Stickiness” – Scientists Develop Potential New Way To Predict Cancer’s Spread
UC San Diego researchers have developed a device that predicts breast cancer aggressiveness by measuring tumor cell adhesion. Weakly adherent cells indicate a higher risk of metastasis, especially in early-stage DCIS. This innovation could [...]
Scientists Just Watched Atoms Move for the First Time Using AI
Scientists have developed a groundbreaking AI-driven technique that reveals the hidden movements of nanoparticles, essential in materials science, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. By integrating artificial intelligence with electron microscopy, researchers can now visualize atomic-level changes that were [...]
Scientists Sound Alarm: “Safe” Antibiotic Has Led to an Almost Untreatable Superbug
A recent study reveals that an antibiotic used for liver disease patients may increase their risk of contracting a dangerous superbug. An international team of researchers has discovered that rifaximin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic [...]
Scientists Discover Natural Compound That Stops Cancer Progression
A discovery led by OHSU was made possible by years of study conducted by University of Portland undergraduates. Scientists have discovered a natural compound that can halt a key process involved in the progression [...]
Scientists Just Discovered an RNA That Repairs DNA Damage – And It’s a Game-Changer
Our DNA is constantly under threat — from cell division errors to external factors like sunlight and smoking. Fortunately, cells have intricate repair mechanisms to counteract this damage. Scientists have uncovered a surprising role played by [...]
What Scientists Just Discovered About COVID-19’s Hidden Death Toll
COVID-19 didn’t just claim lives directly—it reshaped mortality patterns worldwide. A major international study found that life expectancy plummeted across most of the 24 analyzed countries, with additional deaths from cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, and mental [...]
Self-Propelled Nanoparticles Improve Immunotherapy for Non-Invasive Bladder Cancer
A study led by Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) and the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) in South Korea details the creation of urea-powered nanomotors that enhance immunotherapy for bladder cancer. The nanomotors [...]
Scientists Develop New System That Produces Drinking Water From Thin Air
UT Austin researchers have developed a biodegradable, biomass-based hydrogel that efficiently extracts drinkable water from the air, offering a scalable, sustainable solution for water access in off-grid communities, emergency relief, and agriculture. Discarded food [...]
AI Unveils Hidden Nanoparticles – A Breakthrough in Early Disease Detection
Deep Nanometry (DNM) is an innovative technique combining high-speed optical detection with AI-driven noise reduction, allowing researchers to find rare nanoparticles like extracellular vesicles (EVs). Since EVs play a role in disease detection, DNM [...]
Inhalable nanoparticles could help treat chronic lung disease
Nanoparticles designed to release antibiotics deep inside the lungs reduced inflammation and improved lung function in mice with symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By Grace Wade Delivering medication to the lungs with inhalable nanoparticles [...]
New MRI Study Uncovers Hidden Lung Abnormalities in Children With Long COVID
Long COVID is more than just lingering symptoms—it may have a hidden biological basis that standard medical tests fail to detect. A groundbreaking study using advanced MRI technology has uncovered significant lung abnormalities in [...]
AI Struggles with Abstract Thought: Study Reveals GPT-4’s Limits
While GPT-4 performs well in structured reasoning tasks, a new study shows that its ability to adapt to variations is weak—suggesting AI still lacks true abstract understanding and flexibility in decision-making. Artificial Intelligence (AI), [...]
Turning Off Nerve Signals: Scientists Develop Promising New Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
Pancreatic cancer reprograms nerve cells to fuel its growth, but blocking these connections can shrink tumors and boost treatment effectiveness. Pancreatic cancer is closely linked to the nervous system, according to researchers from the [...]