Imagine it is 2030. Doctors in a regional hospital in country X note an expanding cluster of individuals with severe respiratory disease. Rapid whole-genome sequencing identifies the disease-causing agent as a novel coronavirus.
Epidemiological investigations suggest the virus is highly infectious, with most initial cases requiring hospitalisation. The episode bears a striking resemblance to the COVID outbreak first detected in December 2019.
Regional and national health authorities are notified quickly. The national contact point for the International Health Regulations 2024 (a major revision to the current IHR 2005) sends a description to the World Health Organization (WHO). After an intense exchange of information and risk assessment, it declares a public health emergency of international concern.
The outbreak is assigned a response strategy of “elimination”. This designation initiates a well-rehearsed procedure, including mobilising expertise and resource stockpiles.
The elimination response results in localised quarantine measures at the epicentre and its surrounds and a travel freeze across a wide radius within country X and at its borders. It also prompts intensified local and international surveillance. Case numbers rise rapidly but plateau after three weeks, and then fall until no new cases are detected in the community.
After eight weeks of intensive efforts the outbreak is over – similar to the experience of New Zealand, which terminated its initial COVID outbreak in eight weeks using an elimination strategy. The outbreak had spread regionally within country X, but not internationally.
This is how we propose, in The Lancet, the world should respond to future pandemic threats.
An upgraded pandemic response to eliminate at source
The process by which the WHO currently decides whether to declare a public health emergency of international concern (under the International Health Regulations 2005) has drawn criticism for being too slow.
The upgraded response framework we propose would enhance the existing risk assessment by routinely requiring WHO to assign a high-level response strategy for managing this risk. For potential pandemics, we consider this strategy should be elimination rather than suppression or mitigation, which have been the usual default options in the past. In simple terms, “if in doubt, stamp it out.”
The idea of eliminating novel emerging infectious diseases at the earliest possible stage is intuitively appealing and not new. It has been proposed for eliminating novel pandemic influenza outbreaks.
This approach successfully eliminated and then eradicated the SARS pandemic in 2003 (caused by SARS-CoV). It also proved successful in China during early containment of COVID in Wuhan.
We have described this concept previously. Whether this approach could have eliminated and ultimately eradicated COVID, if pursued early and in a co-ordinated way globally, remains a topic of speculation.
An elimination strategy also slows the spread of infection
There is a second broad reason for the WHO assigning an explicit strategic goal of elimination to pandemic diseases with sufficient severity. It can also slow or interrupt the global spread of a new infectious disease. This action buys time for interventions to be developed, building on rapidly accumulating scientific knowledge.
Some countries in the Asia-Pacific region adopted elimination and strong suppression strategies. This approach largely prevented widespread COVID circulation for the first one to two years of the pandemic, keeping mortality rates low.
It allowed time for vaccine development and roll-out and for jurisdictions to prepare their health systems for managing large numbers of infected people. Notable examples are New Zealand, Australia and Singapore. They have been able to keep their cumulative mortality low by international standards.
If elimination is ultimately not successful or justifiable, an organised transition to another strategy (suppression or mitigation) should be considered. Processes for managing these transitions can draw on experience from the current pandemic.
Elimination makes sense for other potential pandemics
The most recently declared public health emergency of international concern is mpox (formerly known as monkeypox). Under our proposed change to the International Health Regulations, the WHO would have been required to assign a response strategy to this disease.
Elimination again makes sense as a default approach. That is what countries around the world have effectively been doing. And this approach appears to be working.
The other current public health emergency of international concern is poliomyelitis. Unlike COVID and mpox, this disease is already subject to a global eradication goal.
A further benefit of the elimination strategy is that it supports strengthening of health system infrastructure in low and middle-income countries. This capacity building has contributed to the elimination of periodic Ebola outbreaks in Africa, which have been designated as public health emergencies of international concern in 2014-16 and 2019-20. It could also support elimination of mpox, an increasing threat in Africa.
Upgraded International Health Regulations could stimulate a huge global investment in infrastructure to stop epidemics at source and improve surveillance capacity. These capacities are critical given the range of future pandemic scenarios, including the threat from bioweapons with advances in synthetic biology.
Let us hope that when the world is next confronted by the spark of a new emerging infectious disease with pandemic potential, the WHO rapidly declares a public health emergency of international concern and assigns an elimination strategy. And the international community reacts vigorously to extinguish the spark before it becomes an inferno.
News
Shocking Amounts of Microplastics in the Brain – It Could Be Increasing Our Risk of Dementia
The brain has higher concentrations of plastic particles compared to other organs, with increased levels found in dementia patients. In a comprehensive commentary published in Brain Medicine, researchers highlight alarming new evidence of microplastic accumulation [...]
Baffling Scientists for Centuries: New Study Unravels Mystery of Static Electricity
ISTA physicists demonstrate that contact electrification depends on the contact history of materials. For centuries, static electricity has intrigued and perplexed scientists. Now, researchers from the Waitukaitis group at the Institute of Science and [...]
Tumor “Stickiness” – Scientists Develop Potential New Way To Predict Cancer’s Spread
UC San Diego researchers have developed a device that predicts breast cancer aggressiveness by measuring tumor cell adhesion. Weakly adherent cells indicate a higher risk of metastasis, especially in early-stage DCIS. This innovation could [...]
Scientists Just Watched Atoms Move for the First Time Using AI
Scientists have developed a groundbreaking AI-driven technique that reveals the hidden movements of nanoparticles, essential in materials science, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. By integrating artificial intelligence with electron microscopy, researchers can now visualize atomic-level changes that were [...]
Scientists Sound Alarm: “Safe” Antibiotic Has Led to an Almost Untreatable Superbug
A recent study reveals that an antibiotic used for liver disease patients may increase their risk of contracting a dangerous superbug. An international team of researchers has discovered that rifaximin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic [...]
Scientists Discover Natural Compound That Stops Cancer Progression
A discovery led by OHSU was made possible by years of study conducted by University of Portland undergraduates. Scientists have discovered a natural compound that can halt a key process involved in the progression [...]
Scientists Just Discovered an RNA That Repairs DNA Damage – And It’s a Game-Changer
Our DNA is constantly under threat — from cell division errors to external factors like sunlight and smoking. Fortunately, cells have intricate repair mechanisms to counteract this damage. Scientists have uncovered a surprising role played by [...]
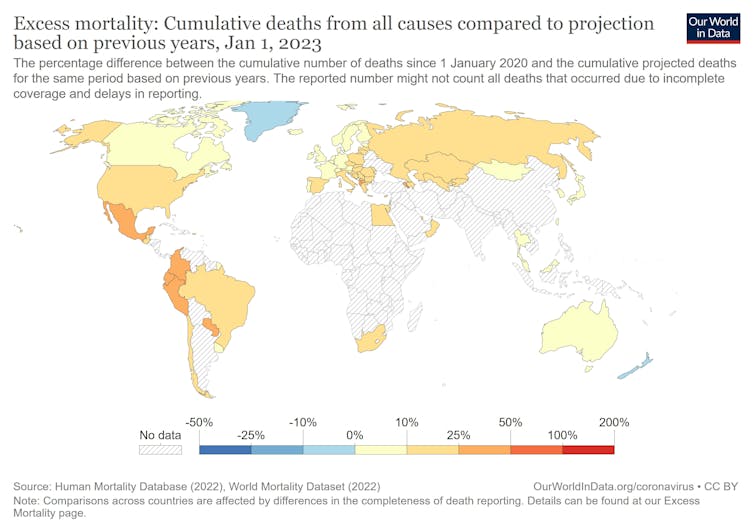
What Scientists Just Discovered About COVID-19’s Hidden Death Toll
COVID-19 didn’t just claim lives directly—it reshaped mortality patterns worldwide. A major international study found that life expectancy plummeted across most of the 24 analyzed countries, with additional deaths from cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, and mental [...]
Self-Propelled Nanoparticles Improve Immunotherapy for Non-Invasive Bladder Cancer
A study led by Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) and the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) in South Korea details the creation of urea-powered nanomotors that enhance immunotherapy for bladder cancer. The nanomotors [...]
Scientists Develop New System That Produces Drinking Water From Thin Air
UT Austin researchers have developed a biodegradable, biomass-based hydrogel that efficiently extracts drinkable water from the air, offering a scalable, sustainable solution for water access in off-grid communities, emergency relief, and agriculture. Discarded food [...]
AI Unveils Hidden Nanoparticles – A Breakthrough in Early Disease Detection
Deep Nanometry (DNM) is an innovative technique combining high-speed optical detection with AI-driven noise reduction, allowing researchers to find rare nanoparticles like extracellular vesicles (EVs). Since EVs play a role in disease detection, DNM [...]
Inhalable nanoparticles could help treat chronic lung disease
Nanoparticles designed to release antibiotics deep inside the lungs reduced inflammation and improved lung function in mice with symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By Grace Wade Delivering medication to the lungs with inhalable nanoparticles [...]
New MRI Study Uncovers Hidden Lung Abnormalities in Children With Long COVID
Long COVID is more than just lingering symptoms—it may have a hidden biological basis that standard medical tests fail to detect. A groundbreaking study using advanced MRI technology has uncovered significant lung abnormalities in [...]
AI Struggles with Abstract Thought: Study Reveals GPT-4’s Limits
While GPT-4 performs well in structured reasoning tasks, a new study shows that its ability to adapt to variations is weak—suggesting AI still lacks true abstract understanding and flexibility in decision-making. Artificial Intelligence (AI), [...]
Turning Off Nerve Signals: Scientists Develop Promising New Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
Pancreatic cancer reprograms nerve cells to fuel its growth, but blocking these connections can shrink tumors and boost treatment effectiveness. Pancreatic cancer is closely linked to the nervous system, according to researchers from the [...]
New human antibody shows promise for Ebola virus treatment
New research led by scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) reveals the workings of a human antibody called mAb 3A6, which may prove to be an important component for Ebola virus therapeutics. [...]