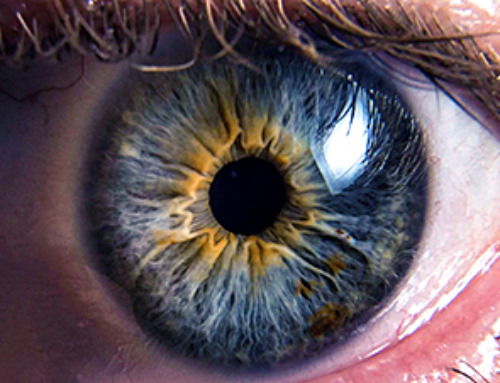
In a recent study published in the journal Science Advances, researchers leveraged crucial aspects of feline eyes, particularly their tapetum lucidum and vertically elongated pupils (VP), to develop a monocular artificial vision system capable of hardware-level object detection, recognition, and camouflage-breaking. While software-aided implementations of object recognition and tracking have been attempted, they require substantial energy and computation requirements, necessitating hardware-level innovations.
The present vision system uses a custom slit-like elliptical aperture (inspired by the asymmetric depth of field of cats’ VPs) to augment object focus and allow for an asymmetric depth of field, improving contrast between the target object and its background. An additional tapetum lucidum-inspired silicon photodiode array with patterned metal reflectors enhances low-light vision. Together, these advancements open the doors to a new generation of mobile robots that can detect, recognize, and track targets with significantly improved accuracy, even in dynamically changing environments with variable lighting conditions.
Background
The 21st century has witnessed unprecedented advancements in robotics and automation, resulting in the gradual influx of robotics across scientific, medical, industrial, and military applications. While software-based machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) deployments have revolutionized robotic automation, hardware-level progress remains shackled by the limitations of conventional design and fabrication decisions.
An ideal example of the above is vision-based operation strategies. Conventional image-capturing devices (e.g., cameras) were optimized to record image data (e.g., light intensity, color, and object shape) but required user input to adjust aperture size and exposure duration to target objects focused under dynamically changing lighting. Modern robotics applications, particularly those used for surveillance, cannot be content with passive image data acquisition. Instead, they need to extract and analyze real-time image data and use this information to guide their subsequent motion.
“However, these tasks become substantially difficult under diverse environments and illumination conditions (e.g., indoor and outdoor and daytime and nighttime). This variability can severely affect the contrast between target objects and their backgrounds, mainly due to pixel saturation under bright conditions and low photocurrent in dark conditions. Objects often create indistinct boundaries with their backgrounds, posing detection and differentiation challenges.”
Software-based computer vision technologies, including high dynamic range (HDR), binocular vision-based camouflage-breaking, and AI-assisted post-processing, have partially addressed the hardware limitations of today’s robotics implementations. Unfortunately, these technologies require substantial computational and energetic (power/electricity) investment, increasing the size and running costs of resulting robotic systems. It is thus imperative for the future of robot automation that hardware capable of unassisted object identification, camouflage-breaking, and optimized performance under a wide range of lighting conditions is developed.
“…animals have adapted themselves to ecologically complex environments for their survival. As a result, distinctive vision systems optimized for their habitats have been developed through long-term evolution. These natural vision systems could offer potential solutions to tackle limitations of conventional artificial vision systems, in terms of depth of field (DoF), field of view (FoV), and optical aberrations.”
About the study
In the present study, researchers developed and tested an artificial vision system that mimics the feline eye. The system comprises two main components: a custom-made optical lens capable of varying apertures between elliptical, small shape, and full-opening circular and a novel hemispherical silicon photodiode array with patterned metal (silver) reflectors (HPA-AgR).
The photodiode array was fabricated by spin coating a silicon dioxide (SiO₂) wafer with a polyamic acid solution containing an ultrathin polyimide (PI) layer upon which a patterned reflector was superimposed using the wet-etching technique (100 nm Ag). The structured reflectors were designed to simulate the light-reflecting properties of the tapetum lucidum, enhancing light absorption under dim lighting conditions. The performance of the resulting photodiode was measured using a wide temperature (3100 K) halogen lamp, a probe station (image sensor array + semiconductor device analyzer), and a data acquisition (DAQ) board.
Monte Carlo-based ray tracing was used to evaluate the camouflage-breaking performance of the feline-inspired vision system versus conventional optical systems (circular pupil [CP]) against a variable lighting of 0-500 lumens.
Study findings
While monocular CP systems (including human eyes) struggle to differentiate between the target object and its background (pixel saturation) in extremely bright scenarios, the asymmetrical aperture design of feline eyes (feline VP) and, by extension, the current vision system can adjust focus between different (tangential and sagittal) planes thereby substantially offsetting light intensity and enabling camouflage breaking.
The design also allows for improved focus on objects at different distances, further reducing optical noise from background elements. Comparisons between the current VP-inspired and conventional CP-like systems highlight the latter’s lack of camouflage-breaking, especially in bright-light conditions. This is predominantly due to observed astigmatism between tangential and sagittal planes, which blurs the target and its background. In contrast, the VP system could easily distinguish between the target and the object irrespective of ambient light intensity. Furthermore, while ‘locked on’ a target, the vision system’s design blurs out the target’s background, reducing the amount of uninformative noise and thereby lowering the computational burden required for real-time analysis.
“Although computer vision and deep learning algorithms have substantially improved handling of noisy targets, the feline eye–inspired vision system provides intrinsic advantages originated from hardware. The feline eye–inspired artificial vision inherently induces background blurring and camouflage breaking, which can markedly reduce the computational burden.”
Similarly, while monocular CP systems achieve high camouflage-breaking performance in low-light conditions (wide-open pupils), they often suffer from low photocurrent in dark scenarios. Feline (and the current artificial) optics circumvent this limitation by not only fully dilating their VPs but also using their tapetum lucidum (or, in the artificial case, their metal reflectors) to reflect ambient light onto the pupil, further enhancing low-light target acquisition. Notably, comparisons between conventional CP optics and the current VP-inspired ones revealed that the novel system is 52-58% more efficient at photoabsorption than traditional technologies.
Despite these advances, the researchers noted one primary limitation of their system: its narrow field of view (FoV). Innovations in optic system movement (possibly inspired by the movements of cat heads) will be needed before these systems can be integrated into autonomous robotics.
Conclusions
The present study reports the development and validation of a novel, feline eye-inspired vision system. The system consists of a variable aperture lens and a metallic silicon photodiode array to achieve unprecedented, hardware-level object tracking and camouflage-breaking irrespective of the intensity of ambient light. While this vision system suffers from a low FoV, advancements in robotic movement may allow for its integration into autonomous robotics, allowing for a new generation of unmanned surveillance and tracking systems.
- Min Su Kim et al. Feline eye–inspired artificial vision for enhanced camouflage breaking under diverse light conditions. Sci. Adv.10, eadp2809 (2024), DOI – 10.1126/sciadv.adp2809, https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adp2809
News
Breakthrough Drug Restores Vision: Researchers Successfully Reverse Retinal Damage
Blocking the PROX1 protein allowed KAIST researchers to regenerate damaged retinas and restore vision in mice. Vision is one of the most important human senses, yet more than 300 million people around the world are at [...]
Differentiating cancerous and healthy cells through motion analysis
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have found that the motion of unlabeled cells can be used to tell whether they are cancerous or healthy. They observed malignant fibrosarcoma cells and [...]
This Tiny Cellular Gate Could Be the Key to Curing Cancer – And Regrowing Hair
After more than five decades of mystery, scientists have finally unveiled the detailed structure and function of a long-theorized molecular machine in our mitochondria — the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier. This microscopic gatekeeper controls how [...]
Unlocking Vision’s Secrets: Researchers Reveal 3D Structure of Key Eye Protein
Researchers have uncovered the 3D structure of RBP3, a key protein in vision, revealing how it transports retinoids and fatty acids and how its dysfunction may lead to retinal diseases. Proteins play a critical [...]
5 Key Facts About Nanoplastics and How They Affect the Human Body
Nanoplastics are typically defined as plastic particles smaller than 1000 nanometers. These particles are increasingly being detected in human tissues: they can bypass biological barriers, accumulate in organs, and may influence health in ways [...]
Measles Is Back: Doctors Warn of Dangerous Surge Across the U.S.
Parents are encouraged to contact their pediatrician if their child has been exposed to measles or is showing symptoms. Pediatric infectious disease experts are emphasizing the critical importance of measles vaccination, as the highly [...]
AI at the Speed of Light: How Silicon Photonics Are Reinventing Hardware
A cutting-edge AI acceleration platform powered by light rather than electricity could revolutionize how AI is trained and deployed. Using photonic integrated circuits made from advanced III-V semiconductors, researchers have developed a system that vastly [...]
A Grain of Brain, 523 Million Synapses, Most Complicated Neuroscience Experiment Ever Attempted
A team of over 150 scientists has achieved what once seemed impossible: a complete wiring and activity map of a tiny section of a mammalian brain. This feat, part of the MICrONS Project, rivals [...]
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area of key focus for the [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is actually broken down into carbon [...]
How Everyday Plastics Quietly Turn Into DNA-Damaging Nanoparticles
The same unique structure that makes plastic so versatile also makes it susceptible to breaking down into harmful micro- and nanoscale particles. The world is saturated with trillions of microscopic and nanoscopic plastic particles, some smaller [...]
AI Outperforms Physicians in Real-World Urgent Care Decisions, Study Finds
The study, conducted at the virtual urgent care clinic Cedars-Sinai Connect in LA, compared recommendations given in about 500 visits of adult patients with relatively common symptoms – respiratory, urinary, eye, vaginal and dental. [...]
Challenging the Big Bang: A Multi-Singularity Origin for the Universe
In a study published in the journal Classical and Quantum Gravity, Dr. Richard Lieu, a physics professor at The University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH), which is a part of The University of Alabama System, suggests that [...]
New drug restores vision by regenerating retinal nerves
Vision is one of the most crucial human senses, yet over 300 million people worldwide are at risk of vision loss due to various retinal diseases. While recent advancements in retinal disease treatments have [...]
Shingles vaccine cuts dementia risk by 20%, new study shows
A shingles shot may do more than prevent rash — it could help shield the aging brain from dementia, according to a landmark study using real-world data from the UK. A routine vaccine could [...]