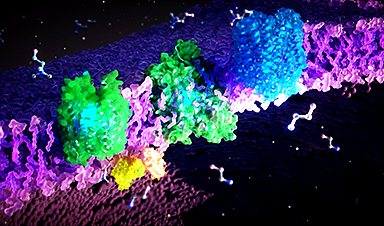
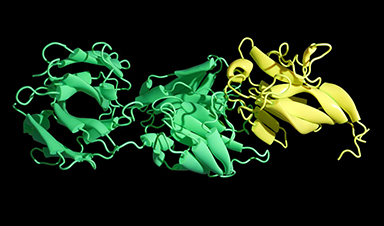
The dynamic structure of FLVCR proteins and their role in nutrient transport within our cells have been revealed.
It is known that malfunctions of the proteins FLVCR1 and FLVCR2 lead to rare hereditary diseases in humans that cause motor, sensory and neurological disorders. However, the biochemical mechanisms behind this and the physiological functions of the FLVCR proteins have been unclear to date.
An interdisciplinary team of researchers from Frankfurt am Main, Singapore and the USA has now deciphered the FLVCR proteins’ 3D structures and their cellular functions. The researchers have shown that the proteins transport the cellular building blocks choline and ethanolamine. Their findings contribute significantly to understanding the pathogenesis of rare diseases and developing new therapies.
In hospital TV series such as Scrubs or Dr. House, medical doctors search for correct diagnoses and possible treatments for patients with sometimes puzzling or strange symptoms. In reality, this process often takes years for those affected by rare diseases. In many cases, there is no effective medication and therapeutic options are limited.
Approximately 6-8% of the world’s population suffers from a rare disease. That’s around 500 million people, even though each of the over 7000 different diseases only affects around one in 2000 people. Since these diseases are so rare, medical and scientific knowledge about them is limited. There are only a few experts worldwide and social awareness is lacking.
Unraveling the structure and function of proteins to understand diseases and develop therapies
An international team of researchers led by Schara Safarian, project group leader at the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics as well as independent group leader at the Fraunhofer Institute for Translational Medicine and Pharmacology ITMP, and the Institute of Clinical Pharmacology at Goethe University Frankfurt, has now investigated the structure and cellular function of two proteins, FLVCR1 and FLVCR2, which play a causal role in a number of rare hereditary diseases. The scientists have published their findings in the prestigious journal Nature.
Malfunctions of FLVCR1 and FLVCR2 due to gene mutations cause rare diseases, some of which result in severe visual, mobility, and sensory disorders – such as posterior column ataxia with retinitis pigmentosa, Fowler’s syndrome or sensory and autonomic neuropathies. The latter can, for example, lead to a complete loss of pain sensation. “In many diseases, including the rare ones, cellular structures in our body are altered and this leads to malfunctions in biochemical processes,” says Schara Safarian. “In order to understand the development of such diseases and develop therapies, we need to know how these proteins are structured at the molecular level and what functions they perform in healthy cells.”
FLVCR1 and FLVCR2 transport the cellular building blocks choline and ethanolamine
The scientists have discovered that FLVCR 1 and FLVCR2 transport the molecules choline and ethanolamine across the membranes of our cells. “Choline and ethanolamine are essential for important bodily functions. They support the growth, regeneration, and stability of our cells, for example in muscles, internal organs, and the brain,” explains Safarian. “Furthermore, choline is involved in fat metabolism and detoxification by the liver. Our body also needs it to produce the neurotransmitter acetylcholine which is crucial for our nervous system and is needed by our brain to control the organs. So, you can imagine that malfunctions of the FLVCR proteins can cause severe neurological and muscular disorders.”
The researchers used microscopic, biochemical, and computer-assisted methods to investigate the FLVCR proteins. “We shock-froze the proteins and then observed them under an electron microscope,” explains Di Wu, a researcher at the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics and co-author of the study. “An electron beam penetrates the frozen sample and the interaction of the electrons with the material creates an image.” The researchers take many individual images and process them and combine them computationally to obtain high-resolution 3D structures of proteins. In this way, they were able to decipher the structures of FLVCR1 and FLVCR2 and see how they change in the presence of ethanolamine and choline. Computer simulations confirmed and visualized how the FLVCR proteins interact with ethanolamine and choline, and dynamically change their structure to enable nutrient transport.
Safarian summarizes: “Our findings pave the way for understanding the development and progression of rare diseases associated with the FLVCR proteins. In the future, patients may be able to benefit from new therapies that restore their life quality.”
Reference: “Molecular mechanism of choline and ethanolamine transport in humans” by Keiken Ri, Tsai-Hsuan Weng, Ainara Claveras Cabezudo, Wiebke Jösting, Yu Zhang, Andre Bazzone, Nancy C. P. Leong, Sonja Welsch, Raymond T. Doty, Gonca Gursu, Tiffany Jia Ying Lim, Sarah Luise Schmidt, Janis L. Abkowitz, Gerhard Hummer, Di Wu, Long N. Nguyen and Schara Safarian, 22 May 2024, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07444-7
News
New Blood Test Detects Alzheimer’s and Tracks Its Progression With 92% Accuracy
The new test could help identify which patients are most likely to benefit from new Alzheimer’s drugs. A newly developed blood test for Alzheimer’s disease not only helps confirm the presence of the condition but also [...]
The CDC buried a measles forecast that stressed the need for vaccinations
This story was originally published on ProPublica, a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive our biggest stories as soon as they’re published. ProPublica — Leaders at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [...]
Light-Driven Plasmonic Microrobots for Nanoparticle Manipulation
A recent study published in Nature Communications presents a new microrobotic platform designed to improve the precision and versatility of nanoparticle manipulation using light. Led by Jin Qin and colleagues, the research addresses limitations in traditional [...]
Cancer’s “Master Switch” Blocked for Good in Landmark Study
Researchers discovered peptides that permanently block a key cancer protein once thought untreatable, using a new screening method to test their effectiveness inside cells. For the first time, scientists have identified promising drug candidates [...]
AI self-cloning claims: A new frontier or a looming threat?
Chinese scientists claim that some AI models can replicate themselves and protect against shutdown. Has artificial intelligence crossed the so-called red line? Chinese researchers have published two reports on arXiv claiming that some artificial [...]
New Drug Turns Human Blood Into Mosquito-Killing Weapon
Nitisinone, a drug for rare diseases, kills mosquitoes when present in human blood and may become a new tool to fight malaria, offering longer-lasting, environmentally safer effects than ivermectin. Controlling mosquito populations is a [...]
DNA Microscopy Creates 3D Maps of Life From the Inside Out
What if you could take a picture of every gene inside a living organism—not with light, but with DNA itself? Scientists at the University of Chicago have pioneered a revolutionary imaging technique called volumetric DNA microscopy. It builds [...]
Scientists Just Captured the Stunning Process That Shapes Chromosomes
Scientists at EMBL have captured how human chromosomes fold into their signature rod shape during cell division, using a groundbreaking method called LoopTrace. By observing overlapping DNA loops forming in high resolution, they revealed that large [...]
Bird Flu Virus Is Mutating Fast – Scientists Say Our Vaccines May Not Be Enough
H5N1 influenza is evolving rapidly, weakening the effectiveness of existing antibodies and increasing its potential threat to humans. Scientists at UNC Charlotte and MIT used high-performance computational modeling to analyze thousands of viral protein-antibody interactions, revealing [...]
Revolutionary Cancer Vaccine Targets All Solid Tumors
The method triggers immune responses that inhibit melanoma, triple-negative breast cancer, lung carcinoma, and ovarian cancer. Cancer treatment vaccines have been in development since 2010, when the first was approved for prostate cancer, followed [...]
Scientists Uncover Hidden Protein Driving Autoimmune Attacks
Scientists have uncovered a critical piece of the puzzle in autoimmune diseases: a protein that helps release immune response molecules. By studying an ultra-rare condition, researchers identified ArfGAP2 as a key player in immune [...]
Mediterranean neutrino observatory sets new limits on quantum gravity
Quantum gravity is the missing link between general relativity and quantum mechanics, the yet-to-be-discovered key to a unified theory capable of explaining both the infinitely large and the infinitely small. The solution to this [...]
Challenging Previous Beliefs: Japanese Scientists Discover Hidden Protector of Heart
A Japanese research team found that the oxidized form of glutathione (GSSG) may protect heart tissue by modifying a key protein, potentially offering a novel therapeutic approach for ischemic heart failure. A new study [...]
Millions May Have Long COVID – So Why Can’t They Get Diagnosed?
Millions of people in England may be living with Long Covid without even realizing it. A large-scale analysis found that nearly 10% suspect they might have the condition but remain uncertain, often due to [...]
Researchers Reveal What Happens to Your Brain When You Don’t Get Enough Sleep
What if poor sleep was doing more than just making you tired? Researchers have discovered that disrupted sleep in older adults interferes with the brain’s ability to clean out waste, leading to memory problems [...]
How to prevent chronic inflammation from zombie-like cells that accumulate with age
In humans and other multicellular organisms, cells multiply. This defining feature allows embryos to grow into adulthood, and enables the healing of the many bumps, bruises and scrapes along the way. Certain factors can [...]