New technology using CRISPR to enhance the immune system's ability to detect cancer cells has been created, potentially paving the way for innovative cancer treatment methods.
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules are an immune complex present on the surface of all cells in humans. MHC class I molecules are a prerequisite for the immune system to recognize and eliminate cancer. When cancer cells are faced with pressure from the immune system, they actively reduce their MHC class I molecules, so cancer cells can hide from drawing the attention of CD8+ T cells, the immune system's primary cancer-fighting cells.
Researchers in Japan and the United States, led by Professor Koichi Kobayashi of Hokkaido University and Texas A&M Health Center, and Dr. Paul de Figueiredo, Bond LSC principal investigator and NEXTGEN Precision Health endowed professor at the University of Missouri, have developed technology to robustly augment the amount of MHC class I in cancer cells. This development, a novel method for boosting the immune system's capability to detect and eliminate cancer cells, was published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Revolutionary Technology for Cancer Immunotherapy
"Our discovery has the potential to transform the way we approach cancer treatment," says Kobayashi. "Our technology enables us to specifically target immune responsive genes and activate the immune system against cancer cells, offering hope to those who are resistant to current immunotherapy."
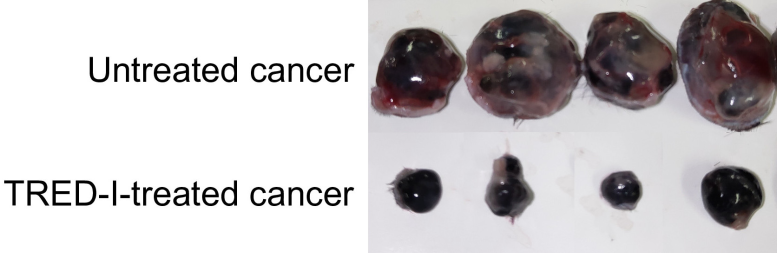
Compared with untreated cancer, the TRED-I system significantly reduced cancer size in mice models. Credit: Xin Sun, et al. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. January 29, 2024
Kobayashi and his team previously identified a gene, called NLRC5, that regulates MHC class I levels. They further found that NLRC5 is suppressed by turning off molecular switches existing on DNA in cancers—through a process called DNA methylation—to reduce levels of MHC class I.
Promising Results and Future Directions
Their technology, known as TRED-I (Targeted Reactivation and Demethylation for MHC-I) system, was able to restore DNA methylation of NLRC5 gene and further activate NLRC5, thus increasing MHC class I levels in cancer without causing severe side effects.
"New modalities for fighting cancer like this are desperately needed because we have few solutions to fight some cancer types," said de Figueiredo. "This is a radically new approach, and I've felt lucky to be part of it."
TRED-I was tested with animal cancer models. It reduced tumor sizes significantly and increased the activity of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells. When used in conjunction with existing immunotherapy, TRED-I markedly enhanced treatment efficacy.
Unexpectedly, the TRED-I system was effective for the tumor distantly located from the original targeted tumor, showing potential to treat metastasized cancers.
"This work is the culmination of our team's research over the past decade," Kobayashi concludes. "It's great to shed light on moving our findings to potential clinical applications. We believe with further refinement, the TRED-I system could contribute significantly to cancer therapy."
Further research will focus on enabling direct delivery of the TRED-I system in cancer patients. Such drugs could improve the efficacy of the immune system in eliminating cancer and would be also able to improve the response to existing therapy.
Reference: "Targeted demethylation and activation of NLRC5 augment cancer immunogenicity through MHC class I" by Xin Sun, Toshiyuki Watanabe, Yoshitaka Oda, Weidong Shen, Alaa Ahmad, Ryota Ouda, Paul de Figueiredo, Hidemitsu Kitamura, Shinya Tanaka and Koichi S. Kobayashi, 1 February 2024, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2310821121
The study was funded by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, the Japan Science and Technology Agency, the Takeda Science Foundation, Bristol-Myers Squibb, the SENSHIN Medical Research Foundation, the Hitachi Global Foundation, the Kobayashi Foundation for Cancer Research, and the Toyo Suisan Foundation.
News
Plastic Without End: Are We Polluting the Planet for Eternity?
The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework calls for the elimination of plastic pollution by 2030. If that goal has been clearly set, why have meaningful measures that create real change still not been implemented? [...]
Scientists Rewire Natural Killer Cells To Attack Cancer Faster and Harder
Researchers tested new CAR designs in NK-92 cells and found the modified cells killed tumor cells more effectively, showing stronger anti-cancer activity. Researchers at the Ribeirão Preto Blood Center and the Center for Cell-Based [...]
New “Cellular” Target Could Transform How We Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
A new study from researchers highlights an unexpected player in Alzheimer’s disease: aging astrocytes. Senescent astrocytes have been identified as a major contributor to Alzheimer’s progression. The cells lose protective functions and fuel inflammation, particularly in [...]
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]