Sensors built with a new manufacturing approach are capable of recording activity deep within the brain from large populations of individual neurons—with a resolution of as few as one or two neurons—in humans as well as a range of animal models, according to a study published in the Jan. 17, 2024 issue of the journal Nature Communications.
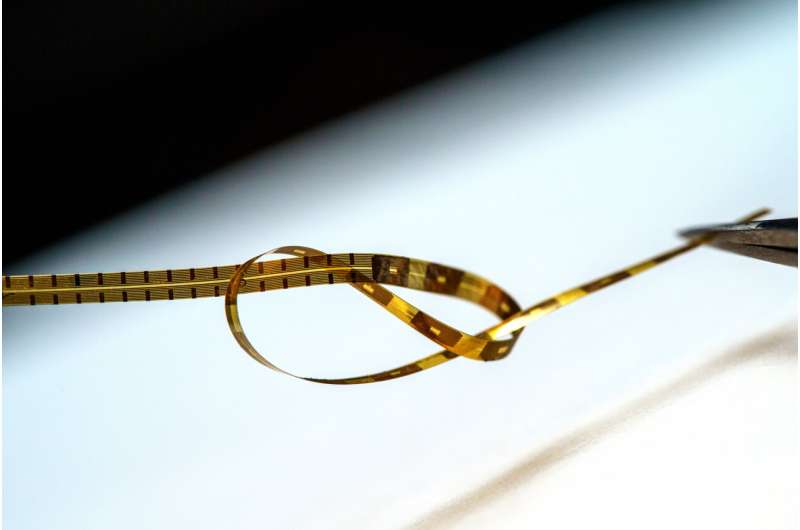
The approach is unique in several ways. It relies on ultra-thin, flexible and customizable probes, made of clinical-grade materials, and equipped with sensors that can record extremely localized brain signals. Because the probes are much smaller than today’s clinical sensors, they can be placed extremely close to one another, allowing for high-resolution sensing in specific areas at unprecedented depths within the brain.
Right now, the probes can record with up to 128 channels, while the state of the art in today’s clinical probes is only eight to 16 channels. In the future, the innovative manufacturing approach the researchers developed can expand the number of channels to thousands per probe, dramatically enhancing physicians’ ability to acquire, analyze and understand brain signals at a higher resolution.
This technology is a first step towards wireless monitoring of patients with treatment-resistant epilepsy for extended periods of time–up to 30 days–as they go about their daily lives. Beyond treatment-resistant epilepsy, the potential applications are much broader, including helping people with Parkinson’s disease, movement disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, obesity, treatment-resistant depression, high-impact chronic pain and other disorders.

While the Nature Communications paper reports brain-recording data only, the system has been developed to both record brain activity and provide electrical stimulation to precise locations. In fact, the team is building on previous—and ongoing—work that uses this scalable, thin-film manufacturing approach to create brain-computer interfaces that record activity and deliver therapeutic electrical stimulation to the surface of the brain cortex.
The probes are monolithic, meaning that their individual components are layered on top of one another to create a single, cohesive unit, and do not require manual assembly of additional wires to conduct recordings.
The new recording system is both extremely customizable and scalable to manufacture, thanks to thin-film technology derived from the semiconductor and digital-display screen industries. As such, the probes are extremely compact—15 microns thick, or about 1/5th the thickness of a human hair—minimizing the differences between the material properties of the probe and the brain.
“We developed an entirely different manufacturing method for thin-film electrodes that can reach deep brain structures—at a depth that is necessary for therapeutic reasons—enabling reproducible, customizable, and high-throughput production of electrodes but with a high spatial resolution and channel count despite a thinner electrode body,” said UC San Diego electrical engineering professor Shadi Dayeh, the corresponding author on the new paper.
“Additionally, the electrode insertion is compatible with existing surgical techniques in the operating room, lowering the barrier for their adoption in clinical procedures.”
The design, manufacture, experimental testing and analysis of results from this system was performed by a cross-disciplinary team of engineers, surgeons, and medical researchers from UC San Diego; Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital; and Oregon Health and Science University.
Dayeh advises two of the three first authors on the paper: UC San Diego postdoctoral researcher Keundong Lee and UC San Diego graduate student researcher Yun Goo Ro. Angelique C. Paulk, also a first author, is a researcher at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in a group led by neurologist Dr. Sydney Cash.
Toward a 30-day wireless brain-recording system
The kind of system researchers developed is needed in order to identify the very specific regions of the brain that are triggering seizures caused by treatment-resistant epilepsy. To meet this goal, the team is working toward their vision of a brain-monitoring system with sensors both inserted deep within the brain and sensors on the surface of the brain.
These sensors will communicate wirelessly with a small computer system in a wireless cap, which a person could wear for extended periods of time. This cap would provide wireless power and the computational infrastructure to capture the brain signals being recorded from a person’s brain for 30 days.
“We are currently focused on applying the technology to patients with treatment-resistant epilepsy. The ultimate goal is to advance the system and related required technologies by 2026 to give patients access to a wireless system that allows them to move freely within the hospital environment and then at home, without being tethered to any machinery, while cortical and deep brain structures are monitored continuously for up to 30 days,” Dayeh said.
The system is called the UC San Diego Micro-stereo-electro-encephalography (µSEEG). The technology that is used to create the device can be manufactured at high volume and low cost because it is derived from existing technologies to manufacture digital display screens, an approach that was originally created by the semiconductor industry. This unique manufacturing process also allows for a series of unique features for these depth electrodes (see sidebar).
Experimental subjects
In the new paper, the team reports the functioning of the new system in two human patients. The team also presents data from a series of different animal models including successful recordings from rat barrel cortex in both acute and chronic settings; recording of the somatosensory cortex in an anesthetized pig; and recordings in non-human primates at different depths inside the brain.
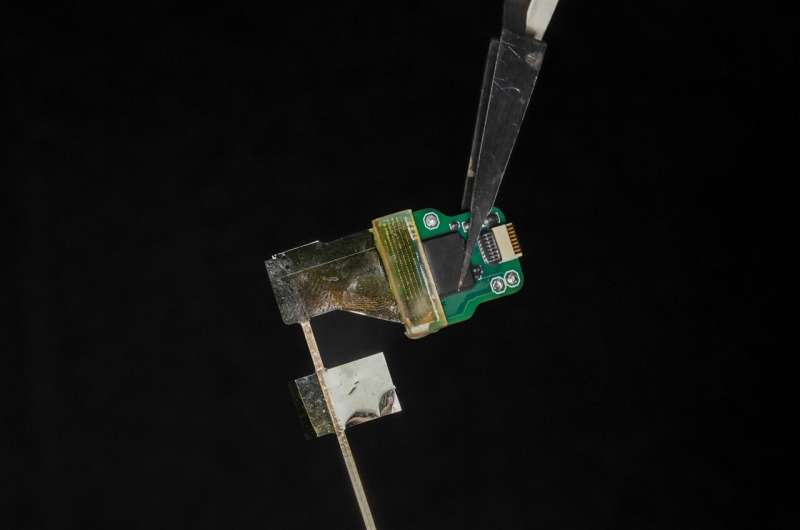
The data on the successful functioning of the device in humans were collected, with all proper approvals and consent, during already scheduled tumor-removal surgeries. During an unrelated pause in the surgery, clinicians inserted the new depth probes into brain tissue that was about to be removed.
“In a true test of the translational feasibility of the µSEEG,” the authors write in the paper, referring to the technical term for their device, “we acutely implanted short 64 channel µSEEG electrodes in the middle temporal gyrus in two separate human patient participants undergoing temporal lobe resection for clinical reasons. With each participant, we inserted a single 64-channel short µSEEG device into tissue, which the clinical team determined would be resected.” The recordings lasted 10 minutes and were able to record ongoing spontaneous activity.
Dr. Keundong Lee, first author and Postdoctoral Fellow at IEBL, UC San Diego said, “It has been a long journey since 2015 to develop a robust, human-grade depth electrode that can be used in clinical practice. Finally, we have discovered an innovative manufacturing technique to create the µSEEG probe, which can assist with high resolution and minimally invasive diagnosis of epilepsy, and potentially treatment for epilepsy and other indications, in the future.”
“Beyond epilepsy, continuous monitoring of brain activity at such high resolution could allow us to find biomarkers for other conditions, including perhaps treatment-resistant depression.”
Dr. Angelique Paulk, Instructor in Neurology at Massachusetts General Research Institute and Harvard Medical School said, “Our lab has worked with the Dayeh lab for almost a decade to bring this innovative technology to fruition. Around 2018, we tested the laminar version of the UC San Diego microSEEG in two patients at MGH.”
“Through iterative feedback that we and Drs. Sharona Ben-Haim, Ahmed Raslan, Mark Richardson, and Ziv Williams provided to inform probe fabrication, we are now happy with the end result that we feel is much closer to clinical use. We were excited to test the longer version in non-human primates here at MGH and to record the activity of single neurons with these devices.”
Dr. Sharona Ben-Haim, MD, Associate Professor of Neurological Surgery, UC San Diego School of Medicine and Surgical Director of Epilepsy, UC San Diego Health added, “This new electrode technology is exciting for a large variety of reasons, including its capacity for recording at unprecedented resolution. The future ability of this system to record wirelessly from the brain of epilepsy patients undergoing intracranial EEG evaluation has the potential to dramatically change our current clinical practice.”
“Currently, patients who undergo this type of evaluation remain in the hospital for the duration of the study, where we try to capture where their unique seizures originate during a period of time that typically lasts from 7–21 days. During this time patients are tethered to their hospital beds by the wired cords from the current clinical electrode system.”
“This new technology has the capacity to potentially allow us to send these patients home, freeing them from a long hospital stay, and potentially allowing us to record for longer periods of time and obtain more robust information to help us ultimately treat their seizures with more precision and resolution than previously possible.”
Features of the UC San Diego micro-stereo-eletro-encephalography (µSEEG)
- The probes can be up to 10 cm in length, allowing for access to structures deep within the brain.
- The probes are incredibly thin: just 15 micron thick, or one-fifth the width of a human hair, and 1.2 millimeters wide
- When inserted into brain tissue, the probe lined with sensors has a thickness that is smaller than technologies currently in clinical use. This smaller thickness means less brain tissue is damaged when the probe is inserted.
- Brain-signal recording electrodes can be placed 60 micrometers apart, which is far closer to each other than technologies currently in clinical use.
- Probes with up to 128 brain-signal-recording channels (electrodes) were demonstrated, compared to eight to 16 recording channels in today’s broadly used clinical depth electrodes.
- The small size of the electrodes allows for extremely localized brain-signal recording, as precise as the signal coming from the individual activity of one or two neurons. They can also record local field potentials, which is aggregate activity of many neurons within a brain region.
- The electrode sensors are able to record precise areas of the brain over both short and long time periods.
- The electrodes work well: they record brain activity triggered by stimulating a body part, and they record the brain dynamics known to occur during anesthesia.
- The system allowed for simultaneous recording of the cortex of the brain and signals from individual neurons deep within the brain. The researchers were able to correlate the general brain activity to what was happening at the single-neuron level.
- The system allows monitoring the dynamics of brain activity instantaneously, allowing visualization of the propagation of the activity across cortical layers with precision with time.
- Cost-effective, scalable manufacturing of the new system is in direct contrast to the expensive and time-consuming manual assembly required for the systems currently in clinical use. All other known experimental depth electrodes require some amount of manual assembly as well.
More information: Keundong Lee et al, Flexible, scalable, high channel count stereo-electrode for recording in the human brain, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-43727-9 , doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-43727-9
News
Treating a Common Dental Infection… Effects That Extend Far Beyond the Mouth
Successful root canal treatment may help lower inflammation associated with heart disease and improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Treating an infected tooth with a successful root canal procedure may do more than relieve [...]
Microplastics found in prostate tumors in small study
In a new study, researchers found microplastics deep inside prostate cancer tumors, raising more questions about the role the ubiquitous pollutants play in public health. The findings — which come from a small study of 10 [...]
All blue-eyed people have this one thing in common
All Blue-Eyed People Have This One Thing In Common Blue Eyes Aren’t Random—Research Traces Them Back to One Prehistoric Human It sounds like a myth at first — something you’d hear in a folklore [...]
Scientists reveal how exercise protects the brain from Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified a biological process that may explain why exercise sharpens thinking and memory. Their findings suggest that physical activity strengthens the brain's built in defense system, helping protect [...]
NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications. A new book from Frank Boehm
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Deadly Pancreatic Cancer Found To “Wire Itself” Into the Body’s Nerves
A newly discovered link between pancreatic cancer and neural signaling reveals a promising drug target that slows tumor growth by blocking glutamate uptake. Pancreatic cancer is among the most deadly cancers, and scientists are [...]
This Simple Brain Exercise May Protect Against Dementia for 20 Years
A long-running study following thousands of older adults suggests that a relatively brief period of targeted brain training may have effects that last decades. Starting in the late 1990s, close to 3,000 older adults [...]
Scientists Crack a 50-Year Tissue Mystery With Major Cancer Implications
Researchers have resolved a 50-year-old scientific mystery by identifying the molecular mechanism that allows tissues to regenerate after severe damage. The discovery could help guide future treatments aimed at reducing the risk of cancer [...]
This New Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Before Tumors Appear
A new CRISPR-powered light sensor can detect the faintest whispers of cancer in a single drop of blood. Scientists have created an advanced light-based sensor capable of identifying extremely small amounts of cancer biomarkers [...]
Blindness Breakthrough? This Snail Regrows Eyes in 30 Days
A snail that regrows its eyes may hold the genetic clues to restoring human sight. Human eyes are intricate organs that cannot regrow once damaged. Surprisingly, they share key structural features with the eyes [...]
This Is Why the Same Virus Hits People So Differently
Scientists have mapped how genetics and life experiences leave lasting epigenetic marks on immune cells. The discovery helps explain why people respond so differently to the same infections and could lead to more personalized [...]
Rejuvenating neurons restores learning and memory in mice
EPFL scientists report that briefly switching on three “reprogramming” genes in a small set of memory-trace neurons restored memory in aged mice and in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease to level of healthy young [...]
New book from Nanoappsmedical Inc. – Global Health Care Equivalency
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
New Molecule Blocks Deadliest Brain Cancer at Its Genetic Root
Researchers have identified a molecule that disrupts a critical gene in glioblastoma. Scientists at the UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center say they have found a small molecule that can shut down a gene tied to glioblastoma, a [...]
Scientists Finally Solve a 30-Year-Old Cancer Mystery Hidden in Rye Pollen
Nearly 30 years after rye pollen molecules were shown to slow tumor growth in animals, scientists have finally determined their exact three-dimensional structures. Nearly 30 years ago, researchers noticed something surprising in rye pollen: [...]
How lipid nanoparticles carrying vaccines release their cargo
A study from FAU has shown that lipid nanoparticles restructure their membrane significantly after being absorbed into a cell and ending up in an acidic environment. Vaccines and other medicines are often packed in [...]





















