Neuroscientists demonstrate how the brain improves its ability to distinguish between similar experiences, findings that could lead to treatments for Alzheimer’s disease and other memory disorders.
Think of a time when you had two different but similar experiences in a short period. Maybe you attended two holiday parties in the same week or gave two presentations at work. Shortly afterward, you may find yourself confusing the two, but as time goes on that confusion recedes and you are better able to differentiate between these different experiences.
New research published today (January 19) in Nature Neuroscience reveals that this process occurs on a cellular level, findings that are critical to the understanding and treatment of memory disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Dynamic Engrams Store Memories
The research focuses on engrams, which are neuronal cells in the brain that store memory information. “Engrams are the neurons that are reactivated to support memory recall,” says Dheeraj S. Roy, PhD, one of the paper’s senior authors and an assistant professor in the Department of Physiology and Biophysics in the Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences at the University at Buffalo. “When engrams are disrupted, you get amnesia.”
In the minutes and hours that immediately follow an experience, he explains, the brain needs to consolidate the engram to store it. “We wanted to know: What is happening during this consolidation process? What happens between the time that an engram is formed and when you need to recall that memory later?”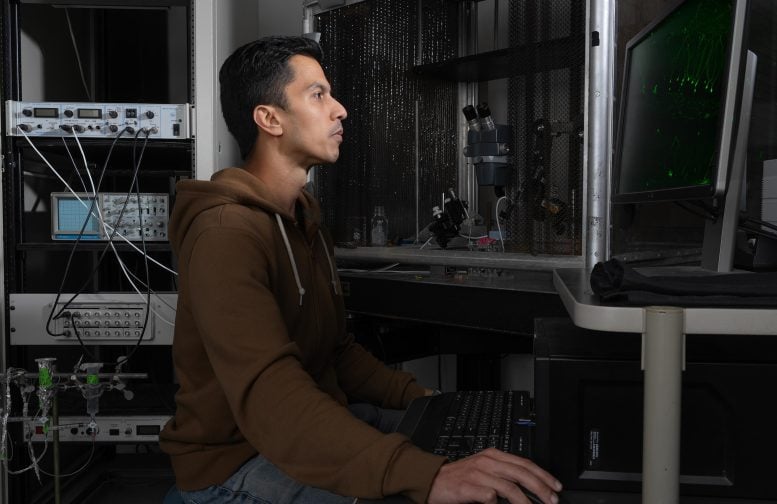
Dheeraj Roy, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Physiology and Biophysics in the Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences at UB, is a senior author on a new paper that explains aspects of how memory works at the cellular level. Credit: Sandra Kicman/Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences
The researchers developed a computational model for learning and memory formation that starts with sensory information, which is the stimulus. Once that information gets to the hippocampus, the part of the brain where memories form, different neurons are activated, some of which are excitatory and others that are inhibitory.
When neurons are activated in the hippocampus, not all are going to be firing at once. As memories form, neurons that happen to be activated closely in time become a part of the engram and strengthen their connectivity to support future recall.
“Activation of engram cells during memory recall is not an all or none process but rather typically needs to reach a threshold (i.e., a percentage of the original engram) for efficient recall,” Roy explains. “Our model is the first to demonstrate that the engram population is not stable: The number of engram cells that are activated during recall decreases with time, meaning they are dynamic in nature, and so the next critical question was whether this had a behavioral consequence.”
Dynamic Engrams Are Needed for Memory Discrimination
“Over the consolidation period after learning, the brain is actively working to separate the two experiences and that’s possibly one reason why the numbers of activated engram cells decrease over time for a single memory,” he says. “If true, this would explain why memory discrimination gets better as time goes on. It’s like your memory of the experience was one big highway initially but over time, over the course of the consolidation period on the order of minutes to hours, your brain divides them into two lanes so you can discriminate between the two.”
Roy and the experimentalists on the team now had a testable hypothesis, which they carried out using a well-established behavioral experiment with mice. Mice were briefly exposed to two different boxes that had unique odors and lighting conditions; one was a neutral environment but in the second box, they received a mild foot shock.
A few hours after that experience, the mice, who typically are constantly moving, exhibited fear memory recall by freezing when exposed to either box. “That demonstrated that they couldn’t discriminate between the two,” Roy says. “But by hour twelve, all of a sudden, they exhibited fear only when they were exposed to the box where they were uncomfortable during their very first experience. They were able to discriminate between the two. The animal is telling us that they know this box is the scary one but five hours earlier they couldn’t do that.”
Using a light-sensitive technique, the team was able to detect active neurons in the mouse hippocampus as the animal was exploring the boxes. The researchers used this technique to tag active neurons and later measure how many were reactivated by the brain for recall. They also conducted experiments that allowed a single engram cell to be tracked across experiences and time. “So I can tell you literally how one engram cell or a subset of them responded to each environment across time and correlate this to their memory discrimination,” explains Roy.”
The team’s initial computational studies had predicted that the number of engram cells involved in a single memory would decrease over time, and the animal experiments bore that out.
“When the brain learns something for the first time, it doesn’t know how many neurons are needed and so on purpose a larger subset of neurons is recruited,” he explains. “As the brain stabilizes neurons, consolidating the memory, it cuts away the unnecessary neurons, so fewer are required and in doing so helps separate engrams for different memories.”
What Is Happening With Memory Disorders?
The findings have direct relevance to understanding what is going wrong in memory disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease. Roy explains that to develop treatments for such disorders, it is critical to know what is happening during the initial memory formation, consolidation and activation of engrams for recall.
“This research tells us that a very likely candidate for why memory dysfunction occurs is that there is something wrong with the early window after memory formation where engrams must be changing,” says Roy.
He is currently studying mouse models of early Alzheimer’s disease to find out if engrams are forming but not being correctly stabilized. Now that more is known about how engrams work to form and stabilize memories, researchers can examine which genes are changing in the animal model when the engram population decreases.
“We can look at mouse models and ask, are there specific genes that are altered? And if so, then we finally have something to test, we can modulate the gene for these ‘refinement’ or ‘consolidation’ processes of engrams to see if that has a role in improving memory performance,” he says.
Reference: “Dynamic and selective engrams emerge with memory consolidation” 19 January 2024, Nature Neuroscience.
DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01551-w
News
How the FDA opens the door to risky chemicals in America’s food supply
Lining the shelves of American supermarkets are food products with chemicals linked to health concerns. To a great extent, the FDA allows food companies to determine for themselves whether their ingredients and additives are [...]
Superbug crisis could get worse, killing nearly 40 million people by 2050
The number of lives lost around the world due to infections that are resistant to the medications intended to treat them could increase nearly 70% by 2050, a new study projects, further showing the [...]
How Can Nanomaterials Be Programmed for Different Applications?
Nanomaterials are no longer just small—they are becoming smart. Across fields like medicine, electronics, energy, and materials science, researchers are now programming nanomaterials to behave in intentional, responsive ways. These advanced materials are designed [...]
Microplastics Are Invading Our Arteries, and It Could Be Increasing Your Risk of Stroke
Higher levels of micronanoplastics were found in carotid artery plaque, especially in people with stroke symptoms, suggesting a potential new risk factor. People with plaque buildup in the arteries of their neck have been [...]
Gene-editing therapy shows early success in fighting advanced gastrointestinal cancers
Researchers at the University of Minnesota have completed a first-in-human clinical trial testing a CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technique to help the immune system fight advanced gastrointestinal (GI) cancers. The results, recently published in The Lancet Oncology, show encouraging [...]
Engineered extracellular vesicles facilitate delivery of advanced medicines
Graphic abstract of the development of VEDIC and VFIC systems for high efficiency intracellular protein delivery in vitro and in vivo. Credit: Nature Communications (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59377-y. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-59377-y Researchers at Karolinska Institutet have developed a technique [...]
Brain-computer interface allows paralyzed users to customize their sense of touch
University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine scientists are one step closer to developing a brain-computer interface, or BCI, that allows people with tetraplegia to restore their lost sense of touch. While exploring a digitally [...]
Scientists Flip a Gut Virus “Kill Switch” – Expose a Hidden Threat in Antibiotic Treatment
Scientists have long known that bacteriophages, viruses that infect bacteria, live in our gut, but exactly what they do has remained elusive. Researchers developed a clever mouse model that can temporarily eliminate these phages [...]
Enhanced Antibacterial Polylactic Acid-Curcumin Nanofibers for Wound Dressing
Background Wound healing is a complex physiological process that can be compromised by infection and impaired tissue regeneration. Conventional dressings, typically made from natural fibers such as cotton or linen, offer limited functionality. Nanofiber [...]
Global Nanomaterial Regulation: A Country-by-Country Comparison
Nanomaterials are materials with at least one dimension smaller than 100 nanometres (about 100,000 times thinner than a human hair). Because of their tiny size, they have unique properties that can be useful in [...]
Pandemic Potential: Scientists Discover 3 Hotspots of Deadly Emerging Disease in the US
Virginia Tech researchers discovered six new rodent carriers of hantavirus and identified U.S. hotspots, highlighting the virus’s adaptability and the impact of climate and ecology on its spread. Hantavirus recently drew public attention following reports [...]
Studies detail high rates of long COVID among healthcare, dental workers
Researchers have estimated approximately 8% of Americas have ever experienced long COVID, or lasting symptoms, following an acute COVID-19 infection. Now two recent international studies suggest that the percentage is much higher among healthcare workers [...]
Melting Arctic Ice May Unleash Ancient Deadly Diseases, Scientists Warn
Melting Arctic ice increases human and animal interactions, raising the risk of infectious disease spread. Researchers urge early intervention and surveillance. Climate change is opening new pathways for the spread of infectious diseases such [...]
Scientists May Have Found a Secret Weapon To Stop Pancreatic Cancer Before It Starts
Researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory have found that blocking the FGFR2 and EGFR genes can stop early-stage pancreatic cancer from progressing, offering a promising path toward prevention. Pancreatic cancer is expected to become [...]
Breakthrough Drug Restores Vision: Researchers Successfully Reverse Retinal Damage
Blocking the PROX1 protein allowed KAIST researchers to regenerate damaged retinas and restore vision in mice. Vision is one of the most important human senses, yet more than 300 million people around the world are at [...]
Differentiating cancerous and healthy cells through motion analysis
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have found that the motion of unlabeled cells can be used to tell whether they are cancerous or healthy. They observed malignant fibrosarcoma [...]