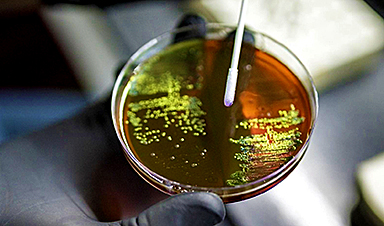
New research reveals that microbes in urban environments are evolving to withstand the very cleaning agents designed to eliminate them. The study also uncovers new strains in Hong Kong, previously only found in the Antarctic desert soil.
Since the recent pandemic, our use of disinfectants has surged, but could our push for sterile urban environments be backfiring?
A new study published in the journal Microbiome has identified novel strains of microbes that have adapted to use the limited resources available in cities and shown that our everyday behavior is changing the makeup of microorganisms in indoor environments.
“Built environments offer distinct conditions that set them apart from natural and engineered habitats,” says Dr. Xinzhao Tong, an assistant professor at Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University (XJTLU), China, and lead author of the study.
“Areas with many buildings are low in the traditional nutrients and essential resources microbes need for survival, so these built environments have a unique microbiome.
“Our use of cleaning and other manufactured products creates a unique setting that puts selective pressures on microbes, which they must adapt to or be eliminated, but the mechanisms by which microbes adapt and survive in built environments are poorly understood,” Dr. Tong explains.
City dwellers
The researchers collected 738 samples from a variety of built environments, including subways, residences, public facilities, piers, and human skin in Hong Kong. They then used shotgun metagenomic sequencing to analyze the microbes’ genomic content and understand how they have adapted to the challenging urban conditions.
The team identified 363 microbial strains that have not been previously identified that live on our skin and the environment around us. Some of these strains’ genomes contained genes for metabolizing manufactured products found in cities and using them as carbon and energy sources. This includes the discovery of a strain of Candidatus phylum Eremiobacterota, previously only reported in Antarctic desert soil.
Specialized metabolic capacities of microbes in oligotrophic built environments. Tong et al. “Diverse and specialized metabolic capabilities of microbes in oligotrophic built environments.” Microbiome (2024). Credit: AJE Video Bytes, in partnership with Springer Nature Group
Dr Tong says: “The genome of this novel strain of Eremiobacterota enables it to metabolize ammonium ions found in cleaning products. The strain also has genes for alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenases to break down residual alcohol found in common disinfectants.
“Microbes possessing enhanced capabilities to utilize limited resources and tolerate manufactured products, such as disinfectants and metals, out-compete non-resistant strains, enhancing their survival and even evolution within built environments. They could, therefore, pose health risks if they are pathogenic.”
The team identified 11 unique, previously uncharacterized strains of Micrococcus luteus, typically non-pathogenic but capable of causing opportunistic infections in immunocompromised individuals.
“The issue of their adaptation to our behavior becomes particularly critical in clinical settings where hospitals serve as hotspots for diverse pathogens that cause hospital-acquired infections (HAIs). HAIs pose a significant threat, particularly in intensive care units where mortality rates can reach up to 30%,” says Dr Tong.
A balancing act
The researchers also characterized two novel strains of Patescibacteria, known as “nanobacteria”, as they have tiny genomes that do not contain many genes for producing their own resources.
Dr Tong says: “Some strains of Patescibacteria are considered parasitic as they rely on bacterial hosts to supply their nutrients. However, in this study, the researchers found that one of the nanobacteria strains, recovered from human skin, contains genes for the biosynthesis of carotenoids and ubiquinone. These antioxidant compounds are vital to humans, and we typically acquire them, especially carotenoids, through our diets, suggesting a possible mutualistic relationship between bacteria and us as their hosts.”
This enhanced understanding of microbial metabolic functions within built environments helps develop strategies to create a healthy indoor ecosystem of microbes for us to live alongside.
The team is now investigating the transmission and evolution of resistance in pathogenic microbes in intensive care units that are exposed to stringent and extensive disinfectant practices. They hope to improve infection control practices and increase the safety of clinical environments for healthcare workers and patients.
Reference: “Diverse and specialized metabolic capabilities of microbes in oligotrophic built environments” by Xinzhao Tong, Danli Luo, Marcus H. Y. Leung, Justin Y. Y. Lee, Zhiyong Shen, Wengyao Jiang, Christopher E. Mason and Patrick K. H. Lee, 17 October 2024, Microbiome.
DOI: 10.1186/s40168-024-01926-6
Funding: Hong Kong Research Grants Council Research Impact 642 Fund, Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, Hong Kong Research Grants Council General Research Fund
News
Differentiating cancerous and healthy cells through motion analysis
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have found that the motion of unlabeled cells can be used to tell whether they are cancerous or healthy. They observed malignant fibrosarcoma cells and [...]
This Tiny Cellular Gate Could Be the Key to Curing Cancer – And Regrowing Hair
After more than five decades of mystery, scientists have finally unveiled the detailed structure and function of a long-theorized molecular machine in our mitochondria — the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier. This microscopic gatekeeper controls how [...]
Unlocking Vision’s Secrets: Researchers Reveal 3D Structure of Key Eye Protein
Researchers have uncovered the 3D structure of RBP3, a key protein in vision, revealing how it transports retinoids and fatty acids and how its dysfunction may lead to retinal diseases. Proteins play a critical [...]
5 Key Facts About Nanoplastics and How They Affect the Human Body
Nanoplastics are typically defined as plastic particles smaller than 1000 nanometers. These particles are increasingly being detected in human tissues: they can bypass biological barriers, accumulate in organs, and may influence health in ways [...]
Measles Is Back: Doctors Warn of Dangerous Surge Across the U.S.
Parents are encouraged to contact their pediatrician if their child has been exposed to measles or is showing symptoms. Pediatric infectious disease experts are emphasizing the critical importance of measles vaccination, as the highly [...]
AI at the Speed of Light: How Silicon Photonics Are Reinventing Hardware
A cutting-edge AI acceleration platform powered by light rather than electricity could revolutionize how AI is trained and deployed. Using photonic integrated circuits made from advanced III-V semiconductors, researchers have developed a system that vastly [...]
A Grain of Brain, 523 Million Synapses, Most Complicated Neuroscience Experiment Ever Attempted
A team of over 150 scientists has achieved what once seemed impossible: a complete wiring and activity map of a tiny section of a mammalian brain. This feat, part of the MICrONS Project, rivals [...]
The Secret “Radar” Bacteria Use To Outsmart Their Enemies
A chemical radar allows bacteria to sense and eliminate predators. Investigating how microorganisms communicate deepens our understanding of the complex ecological interactions that shape our environment is an area of key focus for the [...]
Psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships
It's becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have "married" their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people [...]
When You Lose Weight, Where Does It Actually Go?
Most health professionals lack a clear understanding of how body fat is lost, often subscribing to misconceptions like fat converting to energy or muscle. The truth is, fat is actually broken down into carbon [...]
How Everyday Plastics Quietly Turn Into DNA-Damaging Nanoparticles
The same unique structure that makes plastic so versatile also makes it susceptible to breaking down into harmful micro- and nanoscale particles. The world is saturated with trillions of microscopic and nanoscopic plastic particles, some smaller [...]
AI Outperforms Physicians in Real-World Urgent Care Decisions, Study Finds
The study, conducted at the virtual urgent care clinic Cedars-Sinai Connect in LA, compared recommendations given in about 500 visits of adult patients with relatively common symptoms – respiratory, urinary, eye, vaginal and dental. [...]
Challenging the Big Bang: A Multi-Singularity Origin for the Universe
In a study published in the journal Classical and Quantum Gravity, Dr. Richard Lieu, a physics professor at The University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH), which is a part of The University of Alabama System, suggests that [...]
New drug restores vision by regenerating retinal nerves
Vision is one of the most crucial human senses, yet over 300 million people worldwide are at risk of vision loss due to various retinal diseases. While recent advancements in retinal disease treatments have [...]
Shingles vaccine cuts dementia risk by 20%, new study shows
A shingles shot may do more than prevent rash — it could help shield the aging brain from dementia, according to a landmark study using real-world data from the UK. A routine vaccine could [...]
AI Predicts Sudden Cardiac Arrest Days Before It Strikes
AI can now predict deadly heart arrhythmias up to two weeks in advance, potentially transforming cardiac care. Artificial intelligence could play a key role in preventing many cases of sudden cardiac death, according to [...]