This uncommon process is more frequently observed in neurodegenerative diseases and could offer insights into disease mechanisms.
According to a new study published in PLOS Biology by Kim Hai-Man Chow and colleagues from the Chinese University of Hong Kong, neurons in the brain that re-enter the cell cycle after mitosis are prone to quick senescence, a process observed more frequently in Alzheimer's disease. This discovery provides insight into neurodegeneration and suggests that the methods used can be applied to study other unique cell populations in the brain.
Most neurons in the brain are post-mitotic, meaning they have ceased to divide. For many years, it had been assumed that this post-mitotic state was permanent. Recent discoveries have shown that a small proportion of neurons re-enter the cell cycle, but little is known about their fate after they do.
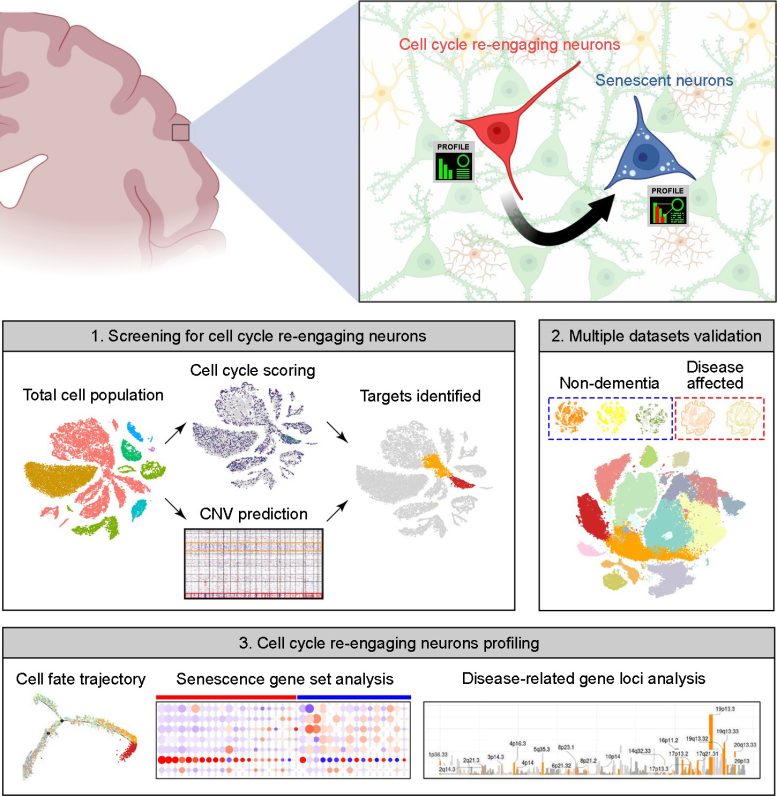
Summary image of the article. The upper part highlights neuronal cell cycle re-engagement is a stage proceeding neuronal senescence and that their full molecular profiles can now be identified by the bioinformatics pipeline we reported in the accepted manuscript. The bottom part is a simplified version of Figure 1A from the paper. The upper panel is created by the BioRender application. Credit: Kim Hei-Man Chow (CC-BY 4.0)
To address this question, the authors turned to publicly accessible databases of "snRNA-seq" data, in which individual single nuclei are isolated and their RNA is sequenced, providing a snapshot of what a cell was doing at the time of isolation. The cell cycle proceeds through distinct phases, including growth, DNA synthesis, division-specific growth, and mitosis, and each phase is characterized by a specific set of proteins required to carry it out. This allowed the authors to use the set of RNAs to tell them which phase of the cycle any specific nucleus was in.
Their data included information on over 30,000 nuclei, each of which was assigned a score based on the level of expression of a set of about 350 cell cycle-related genes. They found that small populations of excitatory neurons had indeed re-entered the cell cycle. These cells did not, for the most part, continue successfully through the cell cycle to produce daughter neurons, however. Instead, cells undergoing re-entry also had elevated expression of genes associated with senescence; in effect, the cells had reawakened only to enter senescence.
Implications for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Intriguingly, the authors found that neurons in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients reentered the cell cycle at a higher rate, and that those neurons that had reentered the cell cycle and aged had increased expression of multiple genes associated with a higher risk of Alzheimer's disease, including those that contribute directly to the production of amyloid, the sticky protein that aggregates in the AD brain. Similarly, brains from patients with Parkinson's disease and Lewy body dementia had an increase in the proportion of re-entering neurons compared to healthy brains.
The neurobiological significance of this heightened re-entry for the diseased brain is still unclear, but the analytical approach taken here may offer deeper insights into neuronal subpopulations within the brain, as well as shedding light on disease mechanisms in neurodegenerative diseases.
"Because of the rare existence and random localization of these cells in the brain, their molecular profiles and disease-specific heterogeneities remain unclear," Chow said. "While experimental validations of these findings in relevant human samples will be conducted in the future, the applicability of this analytical approach in different diseases and cross-species settings offers new opportunities and insights to supplement mainstay histological-based approaches in studying the roles of these cells in brain aging and disease pathogenesis."
The authors add, "This bioinformatics analytical pipeline demonstrated will offer the field a new tool to unbiasedly dissect cell cycle re-engaging and senescent neurons, and to dissect their heterogeneities in healthy versus disease-affected brains."
Reference: "Neuronal cell cycle reentry events in the aging brain are more prevalent in neurodegeneration and lead to cellular senescence" by Deng Wu, Jacquelyne Ka-Li Sun and Kim Hei-Man Chow, 23 April 2024, PLOS Biology.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002559
The work was supported, in part, by grants from the following: The Hong Kong Research Grants Council (RGC)-General Research Fund (GRF) (PI: ECS24107121, GRF16100219 and GRF16100718) (all to K.H-M.C) and the RGC- Collaborative Research Fund (CRF) (Co-I: C4033-19EF) (K.H-M.C); the National NaturalScience Foundation-Excellent Young Scientists Fund 2020 (Ref: 32022087) (K.H-M.C); Alzheimer's Association Research Fellowship (PI: AARF-17-531566) (K.H-M.C).
News
Brain waves could help paralyzed patients move again
People with spinal cord injuries often lose the ability to move their arms or legs. In many cases, the nerves in the limbs remain healthy, and the brain continues to function normally. The loss of [...]
Scientists Discover a New “Cleanup Hub” Inside the Human Brain
A newly identified lymphatic drainage pathway along the middle meningeal artery reveals how the human brain clears waste. How does the brain clear away waste? This task is handled by the brain’s lymphatic drainage [...]
New Drug Slashes Dangerous Blood Fats by Nearly 40% in First Human Trial
Scientists have found a way to fine-tune a central fat-control pathway in the liver, reducing harmful blood triglycerides while preserving beneficial cholesterol functions. When we eat, the body turns surplus calories into molecules called [...]
A Simple Brain Scan May Help Restore Movement After Paralysis
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required. People with spinal cord injuries often experience partial or complete loss of movement in their arms [...]
Plant Discovery Could Transform How Medicines Are Made
Scientists have uncovered an unexpected way plants make powerful chemicals, revealing hidden biological connections that could transform how medicines are discovered and produced. Plants produce protective chemicals called alkaloids as part of their natural [...]
Scientists Develop IV Therapy That Repairs the Brain After Stroke
New nanomaterial passes the blood-brain barrier to reduce damaging inflammation after the most common form of stroke. When someone experiences a stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to the brain to prevent death. [...]
Analyzing Darwin’s specimens without opening 200-year-old jars
Scientists have successfully analyzed Charles Darwin's original specimens from his HMS Beagle voyage (1831 to 1836) to the Galapagos Islands. Remarkably, the specimens have been analyzed without opening their 200-year-old preservation jars. Examining 46 [...]
Scientists discover natural ‘brake’ that could stop harmful inflammation
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have uncovered a key mechanism that helps the body switch off inflammation—a breakthrough that could lead to new treatments for chronic diseases affecting millions worldwide. Inflammation is the [...]
A Forgotten Molecule Could Revive Failing Antifungal Drugs and Save Millions of Lives
Scientists have uncovered a way to make existing antifungal drugs work again against deadly, drug-resistant fungi. Fungal infections claim millions of lives worldwide each year, and current medical treatments are failing to keep pace. [...]
Scientists Trap Thyme’s Healing Power in Tiny Capsules
A new micro-encapsulation breakthrough could turn thyme’s powerful health benefits into safer, smarter nanodoses. Thyme extract is often praised for its wide range of health benefits, giving it a reputation as a natural medicinal [...]
Scientists Develop Spray-On Powder That Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds
KAIST scientists have created a fast-acting, stable powder hemostat that stops bleeding in one second and could significantly improve survival in combat and emergency medicine. Severe blood loss remains the primary cause of death from [...]
Oceans Are Struggling To Absorb Carbon As Microplastics Flood Their Waters
New research points to an unexpected way plastic pollution may be influencing Earth’s climate system. A recent study suggests that microscopic plastic pollution is reducing the ocean’s capacity to take in carbon dioxide, a [...]
Molecular Manufacturing: The Future of Nanomedicine – New book from Frank Boehm
This book explores the revolutionary potential of atomically precise manufacturing technologies to transform global healthcare, as well as practically every other sector across society. This forward-thinking volume examines how envisaged Factory@Home systems might enable the cost-effective [...]
New Book! NanoMedical Brain/Cloud Interface – Explorations and Implications
New book from Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc Founder: This book explores the future hypothetical possibility that the cerebral cortex of the human brain might be seamlessly, safely, and securely connected with the Cloud via [...]
Global Health Care Equivalency in the Age of Nanotechnology, Nanomedicine and Artificial Intelligence
A new book by Frank Boehm, NanoappsMedical Inc. Founder. This groundbreaking volume explores the vision of a Global Health Care Equivalency (GHCE) system powered by artificial intelligence and quantum computing technologies, operating on secure [...]
Miller School Researchers Pioneer Nanovanilloid-Based Brain Cooling for Traumatic Injury
A multidisciplinary team at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine has developed a breakthrough nanodrug platform that may prove beneficial for rapid, targeted therapeutic hypothermia after traumatic brain injury (TBI). Their work, published in ACS [...]